AWS Disaster Recovery Services
Contents
Every day, enterprises face the critical challenge of safeguarding their business data from potential disasters like cyber threats or hardware failures. Data vulnerability becomes a principal concern as companies increasingly rely on online operations. Ensuring the continuity of processes and the integrity of sensitive information demands a robust disaster recovery strategy. AWS disaster recovery services emerges as a reliable and complex solution, offering a suite of tools and technologies designed to fortify data protection and business resilience in the gloss of unforeseen disruptions.
What is the Importance of Disaster Recovery
In the IT industry, a disaster refers to any unexpected event or circumstance that disrupts normal business operations, potentially leading to data loss, system downtime, or service interruptions. These events range from natural disasters and hardware failures to cyberattacks and human errors. Recognizing the inevitability of such disruptions, businesses prioritize Disaster Recovery (DR) as a fundamental component of their risk management strategy.
Disaster recovery is a proactive approach to restore applications post-outage, encompassing three critical components:
- Regarding prevention, the focus is on minimizing the likelihood of technology-related disasters. Businesses establish robust and secure systems, employing tools like system-testing software to prevent configuration errors and failures. While humans cannot control natural disasters, prevention strategies address network issues, security risks, and human errors.
- Anticipation involves the predictive aspect of disaster recovery. Companies develop a comprehensive plan to foresee potential disasters by drawing insights from past incidents. An example of anticipation is the strategic backing up of critical data to the cloud, which pragmatically addresses the prospect of hardware failures, ensuring a proactive approach to data management.
- At last, mitigation is employed after a disaster scenario. The goal here is to minimize the negative impact on routine business procedures. That involves updating documentation, conducting regular disaster recovery testing, identifying manual operating procedures for outages, and coordinating the disaster recovery strategy with relevant personnel.
By holistically addressing prevention, anticipation, and mitigation, enterprises fortify their resilience and readiness, ensuring a prompt and effective response to potential disruptions of IT operations.
There are two primary approaches to Disaster Recovery:
- Traditional backup and restore
This method involves periodic data backups, which are stored in separate locations. In a disaster, the backed-up data is restored to resume operations. However, this method may result in data loss since backups are typically not real-time. - Continuous replication
This procedure ensures the real-time duplication of data to a secondary location. In a disaster, the secondary site takes over seamlessly, minimizing downtime and potential data loss.
Among the many modern solutions for data protection and disaster recovery in networking, cloud DRS services provided by the largest providers, particularly Amazon AWS, stand out. Offering a comprehensive approach, cloud-based Disaster Recovery has several distinct advantages:
- Automated backups
It executes automated backups, streamlining the backup process and ensuring that businesses can quickly restore their databases to a specific point in time, minimizing data loss. - Scalability
Cloud-based DRS services allow businesses to scale resources up or down based on their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance during normal operations and disaster recovery scenarios. - Global accessibility
AWS disaster recovery enables global accessibility. Data can be replicated across multiple regions, providing geographical redundancy and reducing the impact of regional disasters. - Cost efficiency
By leveraging cloud services, businesses can avoid the substantial upfront costs associated with traditional DR infrastructure. Cloud-based solutions offer a pay-as-you-go model, optimizing cost-effectiveness.
Disaster Recovery is not merely a contingency plan but a strategic imperative for businesses in the digital age. Cloud solutions, especially those offered by AWS, enhance the efficiency of Disaster Recovery measures, providing companies with the tools needed to mitigate risks and ensure the continuity of critical operations. Our team values their reliability, often using AWS disaster recovery solutions to design, develop, and deploy our clients’ enterprise applications.

AWS Disaster Recovery Solutions
Amazon Web Services offers a range of techniques tailored to safeguard business data against potential disruptions. Main AWS disaster recovery strategy types address particular recovery needs utilizing specific DRS tools.
Backup and Restore
The Backup and Restore strategy is a robust approach to mitigate against data loss or corruption. This method is particularly effective for scenarios where safeguarding against the disruption or loss of a physical data center is the primary concern.
The strategy involves the periodic or continuous backup of critical workload data. AWS provides various services dedicated to this purpose, including Amazon EBS snapshot, Amazon DynamoDB backup, Amazon RDS snapshot, and more. They ensure companies can achieve their desired Recovery Point Objective (RPO) by determining how often backups are executed.
However, this approach extends beyond data replication. It necessitates the redeployment of the entire infrastructure, including configuration and application code, in the recovery Region. To facilitate rapid and error-free redeployment, infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tools such as AWS CloudFormation or the AWS Cloud Development Kit are recommended. They play a key role in simplifying the restoration process by automating the setup of the infrastructure.
Ensuring a comprehensive recovery strategy, Backup and Restore emphasizes the need to back up user data and code and configuration elements. That includes creating Amazon Machine Images for Amazon EC2 instances, which are essential for launching restored instances in the recovery region.
Furthermore, AWS Backup is a centralized platform for configuring, scheduling, and monitoring backup capabilities across various services like Amazon EBS volumes, Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon RDS databases, and more. The ability to copy backups across regions adds an extra layer of resilience, facilitating disaster recovery on a global scale.
As part of this strategy, AWS encourages enterprises to adopt a continuous testing approach to confirm the completeness of the implementation. Testing, particularly in disaster recovery, ensures the backup strategy is reliable and aligned with the desired recovery objectives.
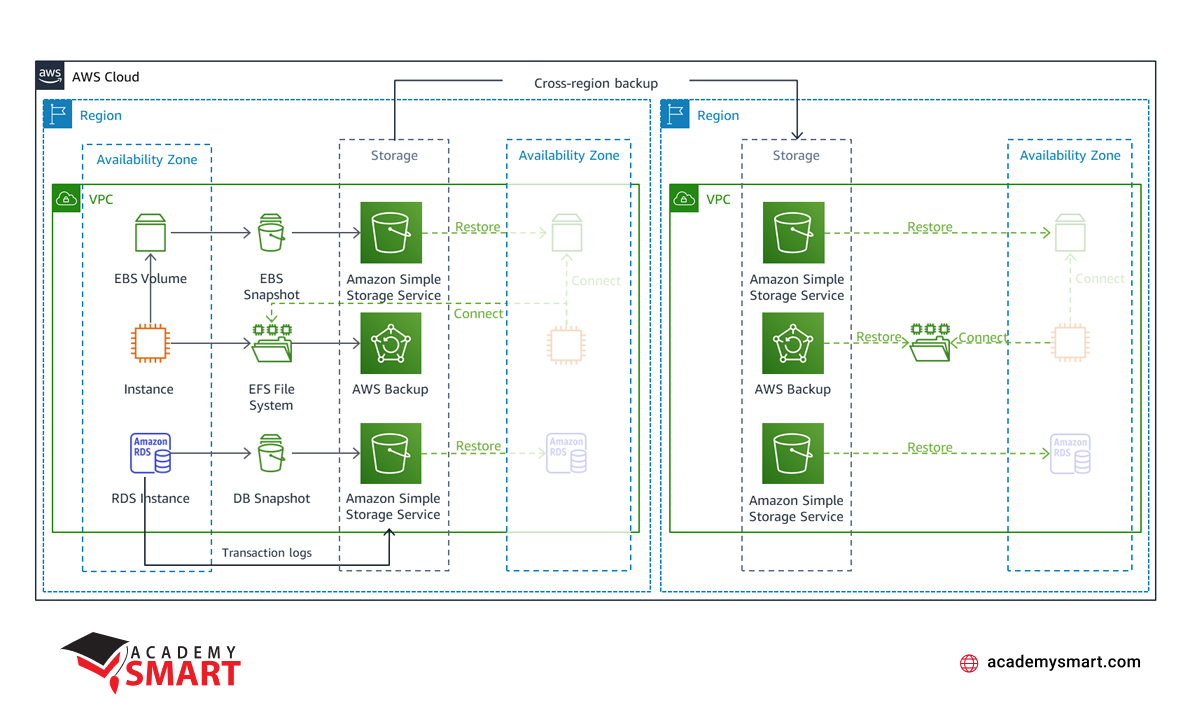
AWS disaster recovery Backup and Restore strategy
Pilot Light
Pilot Light is an AWS disaster recovery procedure that involves maintaining a scaled-down, fully functional copy of a production environment in another region. In the Pilot Light model, resources required to support data replication and backup, such as databases and object storage, are kept in a “switched-off” state and are only activated during testing or when disaster recovery failover is initiated.
This strategy extends the Elastic Disaster Recovery concept, where data is constantly replicated to a staging area subnet in your AWS account. In the event of a failover, the staged resources are used to automatically create a full-capacity deployment in the target Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) designated as the recovery location. This staged approach minimizes ongoing costs by keeping only essential resources active and simplifies retrieval during a disaster.
While the Elastic Disaster Recovery component continuously replicates data, the Pilot Light strategy focuses on maintaining a ready-to-activate infrastructure, reducing costs and complexities associated with keeping all resources fully active. It balances between minimizing ongoing expenses and ensuring fast recovery by activating only the essential components during a disaster.
Automation tools such as AWS CloudFormation can be employed to implement the Pilot Light approach effectively. They allow for compatible deployment of infrastructure across multiple AWS accounts and regions. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) ensures that the necessary resources are deployed reliably, enabling quick provisioning of a full-scale production environment when needed.
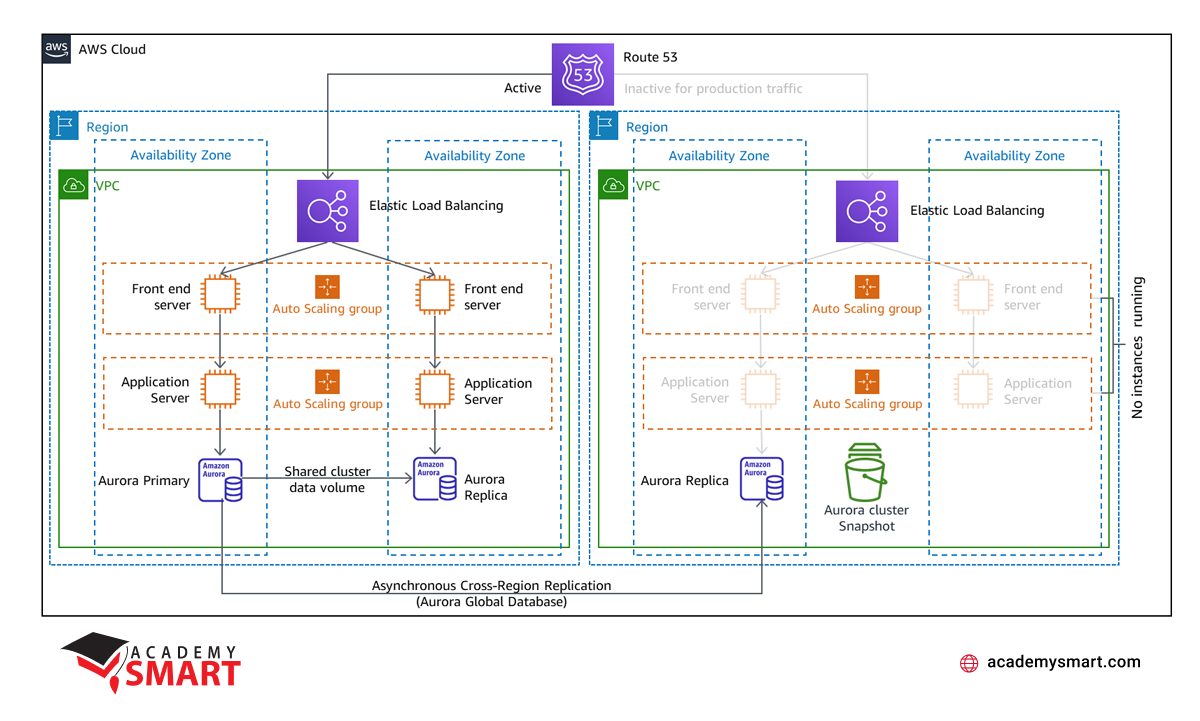
AWS disaster recovery Pilot Light strategy
Warm Standby
Warm Standby is a DR strategy that builds upon the concepts of Pilot Light, also offering a copy of a production environment in another region. In this case, the key distinction lies in that the Warm Standby model always keeps the workload on in the secondary area. Unlike Pilot Light, where certain components are in a “switched-off” state and activated as needed, Warm Standby maintains a state of readiness with resources constantly deployed and running.
The Warm Standby scheme ensures that the essential elements of your production environment, including application servers, are active and available at reduced capacity levels in the designated disaster recovery region. This constant readiness allows for quicker recovery times, as there is no need to activate specific resources during a failover event.
To facilitate the scaling of resources within the Warm Standby approach, tools like Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling are employed. They provide the dynamic adjustment of resources, including EC2 instances, tasks in Amazon ECS, and throughput in Amazon DynamoDB within an AWS region. Scaling is crucial to ensure the disaster recovery region can promptly handle the complete production load.
While Warm Standby is more resource-intensive than Pilot Light due to the continuous availability of essential components, it offers advantages in terms of reduced recovery times and the ability to perform testing or constant testing, increasing confidence in the recovery process. The decision to choose between Pilot Light and Warm Standby often hinges on specific Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) needs, with Warm Standby providing a faster response to disasters by maintaining an “always-on” infrastructure.
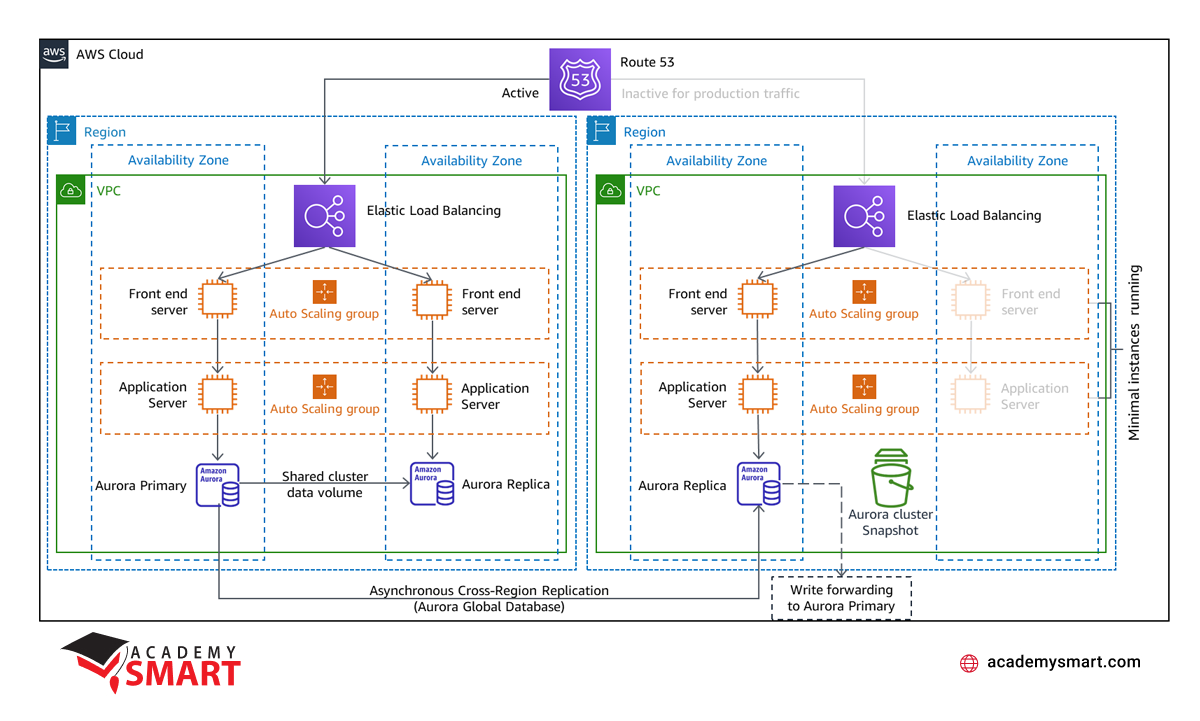
AWS disaster recovery Warm Standby strategy
Multi-Site Active/Active
The advanced disaster recovery strategy involves running a workload simultaneously in multiple regions. In this approach, the workload actively serves traffic from all the areas where it is deployed, creating a highly resilient and geographically distributed system. Compared to other disaster recovery strategies, there is no concept of failover in Multi-Site Active/Active since the workload operates concurrently in more than one region.
This strategy is the most complex and costly among disaster recovery approaches. Still, it can achieve near-zero recovery times for most disasters, provided the right technology choices and implementation are in place. But, to be effective, it requires careful consideration of data consistency, especially in write operations within such a distributed IT ecosystem.
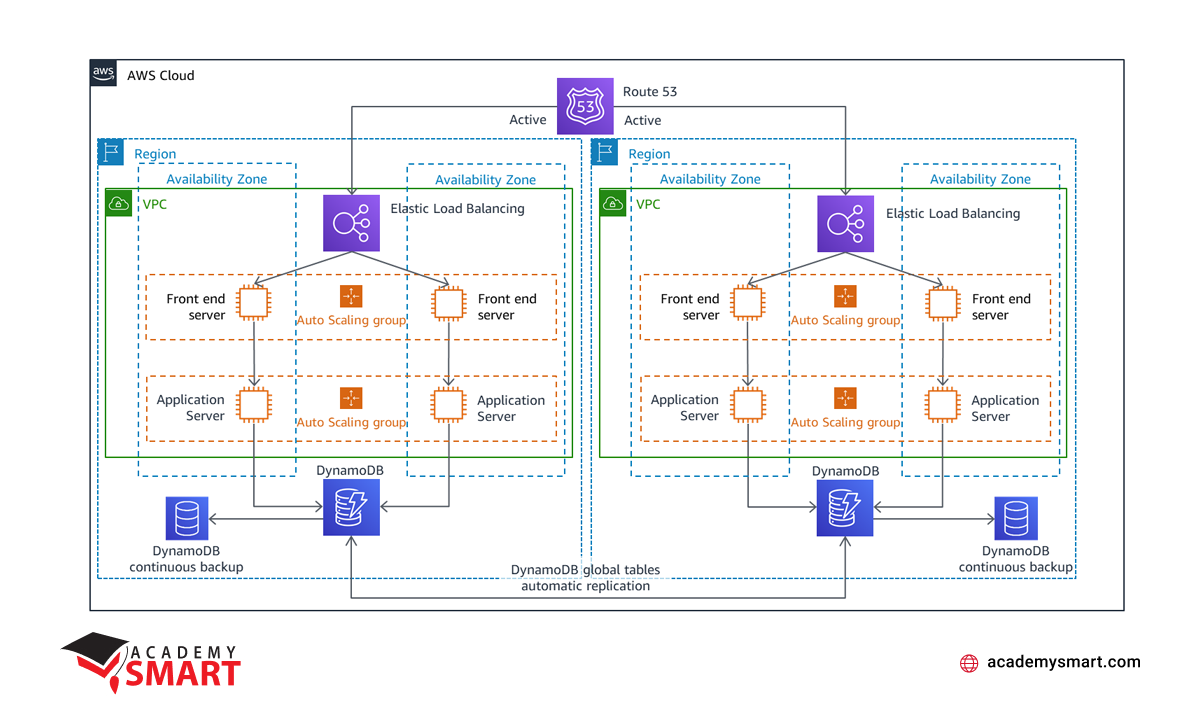
AWS disaster recovery Multi-Site Active/Active strategy
AWS Disaster Recovery Plan Template
A disaster recovery plan is an integral part of the requirements for software application development in the cloud. It is a comprehensive guide outlining key elements that are crucial for an effective disaster recovery strategy. It encompasses internal and external communication, defining roles and responsibilities within the team responsible for the plan. Clear communication channels with employees, customers, and team members are established to ensure a coordinated response during a disaster.
One essential aspect covered in the template is establishing a recovery timeline. That includes defining goals and time frames for returning systems to normal operations after a disaster. The recovery timeline addresses two key objectives: the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and the Recovery Point Objective (RPO). RTO determines the maximum acceptable time for completing disaster recovery, varying based on impacted IT infrastructure. RPO sets the maximum acceptable time for data loss after a disaster, influencing the frequency and method of data backups.
Data backups are a critical component of the disaster recovery plan, and the template guides how to synchronize and back up data. It explores cloud storage, vendor-supported backups, and internal offsite data backups. Emphasis is placed on ensuring that backups are not stored onsite to account for natural disaster events.
Testing and optimization are integral to the plan, with a recommendation to conduct tests at least once or twice yearly. Regular testing allows for identifying and resolving any gaps in the disaster recovery plan. Additionally, the template emphasizes the importance of updating security and data protection strategies to prevent unauthorized access.
When your business application is deployed to Amazon Cloud, the disaster recovery plan template should integrate best practices, aligning with AWS principles articulated in the AWS Well-Architected Framework.
Ensure AWS Disaster Recovery Best Practices with Our Help
At Academy Smart, we bring our custom software development know-how to provide a thorough solution for implementing cloud computing in enterprises. With our IT outstaffing services, you can access adept programmers and DevOps specialists to develop and maintain cloud-native and hybrid applications. Connect with us to discuss your project vision and requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions: AWS Disaster Recovery
What is AWS elastic disaster recovery?
AWS elastic disaster recovery is a service that continuously replicates server-hosted applications and databases from any source into AWS Cloud.
What are the main AWS disaster recovery types?
- Backup and Restore;
- Pilot Light;
- Warm Standby;
- Multi-Site Active/Active.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!