Cloud service deployment options: Private vs Public Cloud
Contents
Introduction
Infrastructure deployment approaches are not cast in stone, so when an organization needs to grow and evolve, you can select between several viable approaches, namely between public and private cloud services. However, to ensure a successful transition to the cloud you should clearly identify the difference between public and private cloud services:
- public cloud infrastructure services are taken from a common pool and shared by all the users, who cannot precisely configure them to their needs and have to work with pre-configured packages
- private cloud computing services are delivered through a separated sector of a public cloud infrastructure, where a single organization uses the bandwidth, data storage, and networking — and can configure these parameters the way they need to.
Thus, this article compares 2 main cloud deployment options: private cloud vs public cloud. Read on to learn the pros and cons of both approaches.
What is Public Cloud?
What is the public cloud services model? It is the most popular type of cloud deployment, where servers, storage and networking are owned and maintained by the cloud service provider (or CSP). AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, DigitalOcean are all examples of public cloud services.
The key benefits of public cloud infrastructure are as follows:
- High-availability and scalability
- Affordable subscription-based multi-tiered pricing
With this approach, every public cloud user shares the same hardware, storage, and networking devices with other users (or “tenants”). Resources are managed via web-based dashboards within the limits of the subscription plan. Public cloud infrastructure is often used to run SaaS apps, host web-based email solutions, data storage, etc.
When to use Public Cloud?
Below are the most popular public cloud use cases:
- Predictable workloads and cloud computing resource needs, like communication services for a known quantity of users
- Running apps and services required to conduct IT and business workflows
- Scaling up and down to meet periodic workload spikes
- Environments for software development and testing
Pros of Public Cloud
The public cloud provides some significant advantages to its tenants:
- Cost reduction. By selling their infrastructure to multiple tenants at once and managing the workloads, cloud service providers maximize the efficiency of hardware usage, thus minimizing the costs for every tenant. Besides, all the CAPEX are split between all the users, so they become negligible in comparison with maintaining an on-prem data center.
- Scalability. With cloud platforms, adding new instances or removing the unneeded ones is done in minutes and seconds, not hours and days.
- Simplified server management. Depending on whether you use IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, or serverless levels of the cloud infrastructure, your IT team spends less and less effort managing the servers and can dedicate more time to deliver more business value.
- Cybersecurity. Smaller businesses might lack the resources needed to build impenetrable cybersecurity defenses. By using public cloud services, they kinda outsource the task to a partner with more resources. Besides, CSPs provide a wide range of security features that enable you to protect your business.
Cons of Public Cloud:
- Data location and compliance concerns. Heavily-regulated industries and organizations like governmental bodies have to meet strict data security and compliance requirements. For example, they have to store their sensitive data within the boundaries of their country, which is hard to ensure in the public cloud.
- Vendor lock-in. All cloud service providers make it a point that you can build everything you need using their services and features. However, the more you use the more you pay, not to mention the need to rebuild everything from scratch should you ever decide to switch to another provider.
What is a Private Cloud?
When a business wants to benefit from the scalability and security of the cloud but does not want to rely on third-party admin staff to run their infrastructure, they can opt for a private cloud solution. It can be physically located at your on-prem data center (so-called hybrid cloud) or run on a cloud service provider’s hardware — but all the resources are dedicated solely to you and you are responsible for their configuration. For example, IBM Cloud provides a wide range of products and services for building on-prem and private cloud solutions, making it the best private cloud service provider.
The main advantages of private cloud solutions involve:
- Scalability of the cloud combined with the security of on-prem data center
- Full control over the computing resources usage and data processing
When to use Private Cloud?
Using the private cloud is the best choice for such situations:
- Data storage for strictly regulated industries like government or healthcare
- Handling sensitive data
- Data processing in companies that execute strict control over their IT infrastructure and workloads to ensure regulatory compliance, like banking
- Global enterprises with geographically dispersed data storage and processing operations, that need to optimize their workflows to ensure cost-efficiency
- Top-performing organizations that can afford to invest in innovative technologies to ensure data processing speed and high-availability
Pros of Private Cloud:
- Better scalability — you gain cloud scalability and speed of operations vastly surpassing on-prem capacities
- Better flexibility — from faster instance provisioning and configuration to the ability to building CI/CD pipelines for software delivery and management, private cloud offers great flexibility
- Better security — you fully control the access to your cloud computing resources, their allocation and usage
Cons of Private Cloud
- Costs. Off-the-shelf private cloud solutions have higher TCO as compared to the public cloud, which makes them not the best choice for short-term projects
- Mobile accessibility. Configuring access to private cloud resources from mobile devices might be quite complicated
- Scalability limitations. If your private cloud is deployed to your on-prem datacenter, you are still limited by its capacity
Which deployment option to choose for a cloud strategy?
While you are most likely using cloud computing in some form already, there rarely are either/or situations in business. The choice between public or private cloud mostly depends on regulatory requirements and is determined by particular aspects of the inherent value proposition. You either save money but have to rely on the cloud provider to deliver the needed resources — or you pay for a certain amount of resources that are always at your disposal.
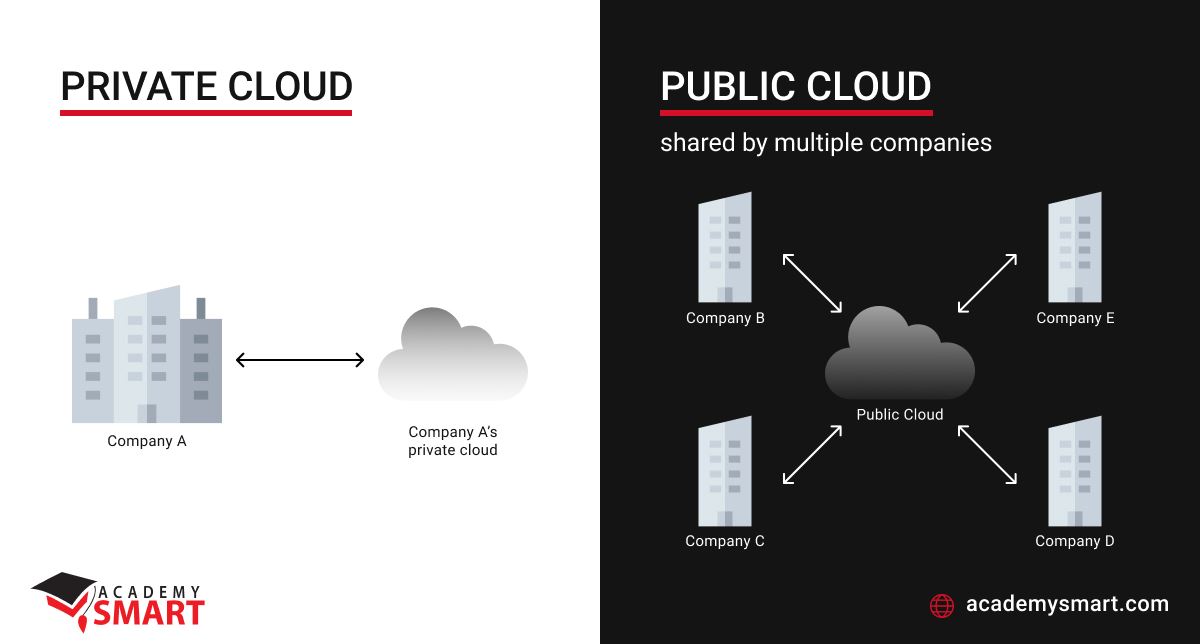
The public cloud provides all users with access to a pool of commonly accessible resources. If they need more, they order more and get the needed instances in seconds or minutes. When the users do not need these instances, they cancel them and the resources are returned to the pool. Thus, theoretically, a situation might arise when there are not enough resources in the pool, but it is practically impossible. This way, all cloud users get access to inexpensive computing resources.
In the private cloud, you pay for a certain amount of resources, either an isolated sector of a public cloud or through an off-the-shelf on-prem solution. You share resources with no one, but the TCO is higher, both due to additional security configuration and for underutilized resources that you have to pay for.
Summary
The choice between public or private cloud deployment depends mostly on your long-term IT strategy needs and business preferences. If your business does not operate in a heavily-regulated industry like healthcare and you do not have to take excessive security measures to protect your sensitive data — the public cloud can provide all the security, cost-efficiency, and scalability you need.
On the other hand, a private cloud provides an extra security layer to meet regulatory compliance requirements, while still delivering the performance needed to meet your business objectives. In addition, many enterprises combine their on-prem clouds for storing mission-critical sensitive data with customer-facing public cloud infrastructure to process customer requests. This is so-called “hybrid” cloud deployment, providing a combination of public and private cloud benefits.
Should your business need assistance with forming and implementing the best cloud strategy for your particular case, IT company Academy Smart can provide a dedicated team of skilled DevOps/Cloud computing specialists to cover all your requests:
Share your challenges with us! https://academysmart.com/get-in-touch/
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!