Multi-Tenant Cloud Computing
Contents
The utilization of cloud computing has emerged as a notable force, reshaping the way organizations operate and innovate. It represents a paradigm shift from traditional on-premises infrastructure to a dynamic, scalable, and cost-effective model that aligns seamlessly with the agility required in today’s competitive marketplace. One popular cloud computing solution that merits business attention is the concept of multi-tenancy. This article describes the specificity of that cloud software engineering approach.
What is a Tenant in Cloud Computing
In cloud computing, a “tenant” refers to an individual or organization that uses the services and resources provided by a cloud service vendor. It’s a customer or user renting space and computing power in the cloud to run applications, store data, or perform various tasks within a cloud platform or infrastructure.
There are two typical scenarios for interacting enterprises with cloud computing power:
- to rent dedicated servers or resources exclusively for own use – a single tenancy;
- to share the same pool of resources on the cloud server with other customers, getting isolated work space but a common underlying infrastructure – a multitenancy.
In a public cloud setting, multi-tenancy is a fundamental characteristic. Multiple users, known as tenants, share the same infrastructure and services a cloud service supplier provides. The resources are dynamically allocated and shared among various tenants, allowing for cost efficiency and scalability. Multi-tenancy is a cost-effective solution where tenants benefit from public cloud shared infrastructure and services, but customization options may be more limited compared to private clouds.
Private clouds, on the other hand, belong to one client and are mostly single-tenant solutions. However, multi-tenancy can still be implemented within a private cloud, especially in large enterprises with diverse business units or departments. In this case, different divisions or teams within the company act as separate tenants, sharing the common infrastructure while maintaining isolation. Private cloud multi-tenancy offers greater control, customization, and security than public clouds, making it suitable for enterprises with specific regulatory or compliance requirements.
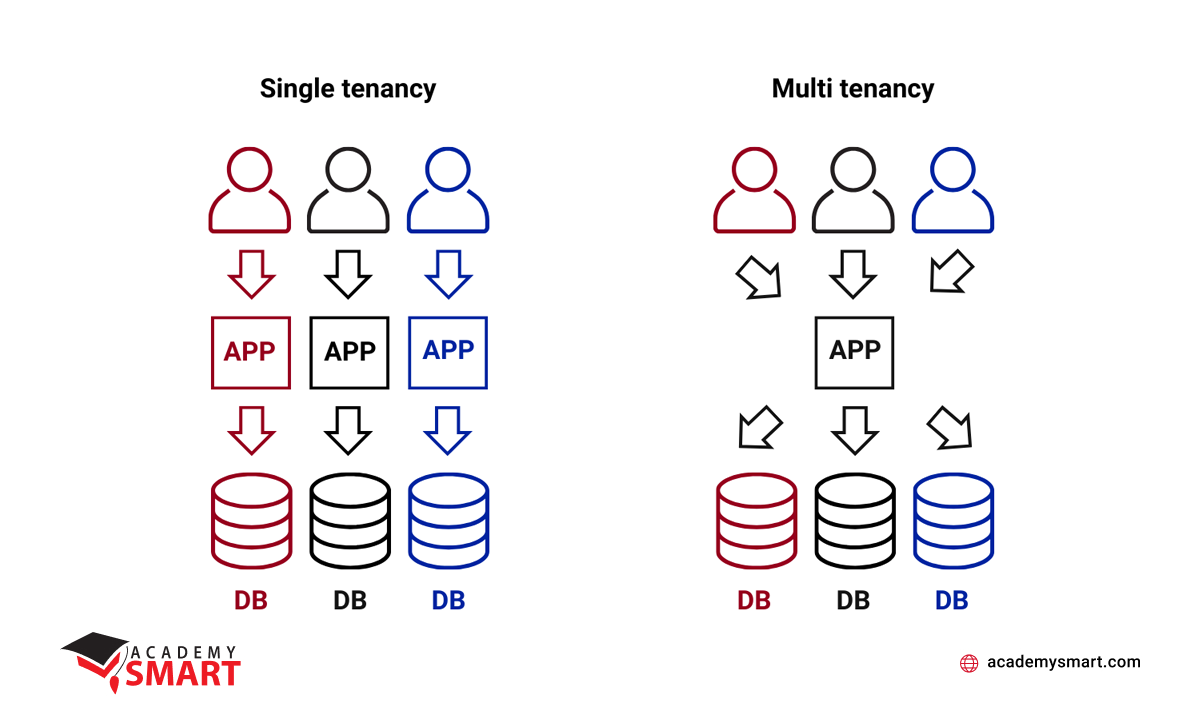
Single vs multi tenant cloud concepts
Single tenant vs. multi-tenant environment: pros and cons
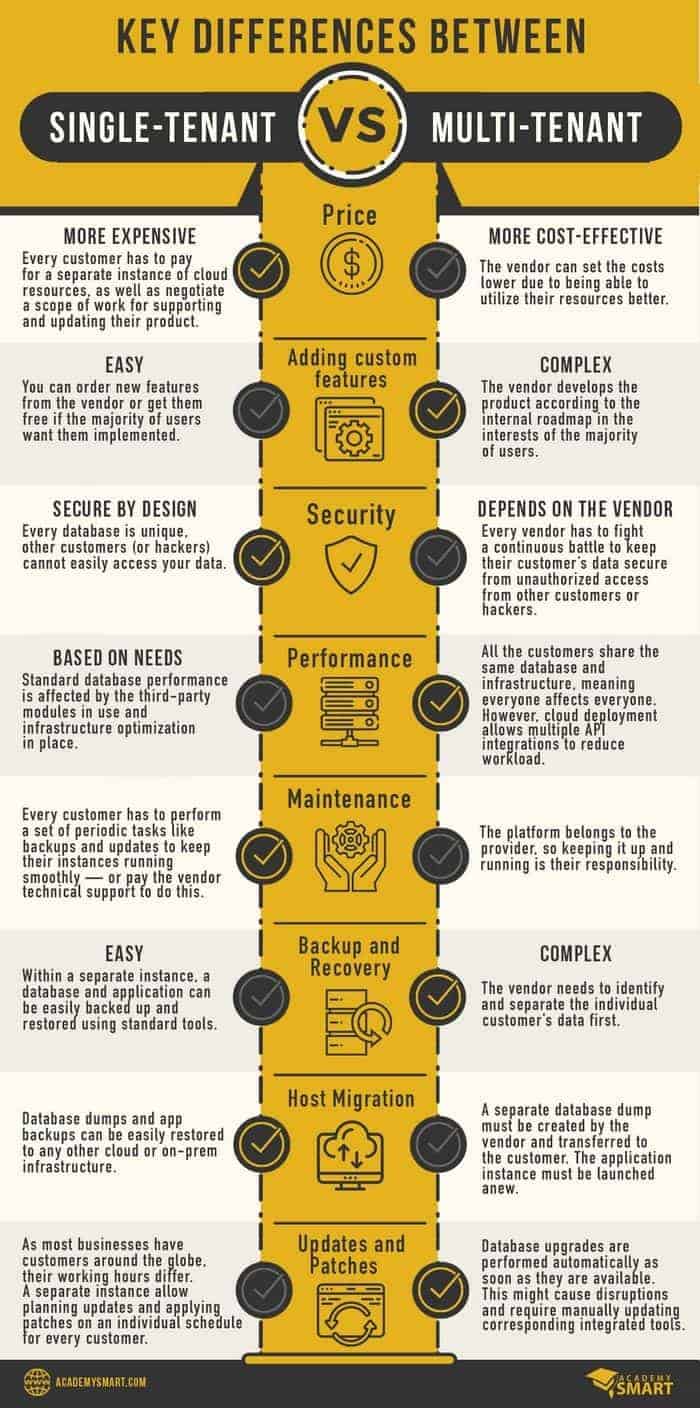
The sole user or company owns the entire cloud infrastructure in a single-tenant environment. This exclusivity extends to hardware, virtual machines, software applications, and data storage. Each tenant operates in an isolated cloud system, enjoying complete control over resources, security parameters, and infrastructure management. This specificity allows for a personalized experience, making single-tenant setups ideal for enterprises with stringent data privacy requirements, specific compliance needs, or those seeking comprehensive customization.
At the same time, single-tenant cloud solutions are typically more expensive due to dedicated resources, making them less cost-effective than multi-tenant propositions. Clients may experience when their usage patterns don’t align with the allocated resources, resulting in underutilization and overpayment. Finally, single-tenant applications require deploying and managing instances for each customer, becoming more challenging for cloud service vendors with a growing clientele.
Conversely, a multi-tenant environment hosts multiple customers on the same physical hardware or software instance. This shared infrastructure promotes efficiency through the optimal utilization of resources. Tenants benefit from a cost-effective model where expenses, maintenance, and updates are divided among them. While each tenant operates in an logically isolated workspace, the underlying infrastructure, serverless components, platform, and software services are communal.
Multi-tenancy is integral to effective SaaS operations. Supported by cloud services like AWS, it provides tools for faster application development, deployment, and scaling, allowing SaaS providers to serve multiple clients efficiently with a shorter cloud software development life cycle. Moreover, multi-tenant architectures automate the onboarding process, making it convenient and efficient for new tenants to sign up and configure their environments.
There are two primary types of multi-tenant architectures:
- One app instance, one database
In this model, a single instance of the software supports individual databases for each tenant. It is easy to scale as capacity increases with the number of tenants, but resource allocation management is more complex. Moreover, the “noisy-neighbor” effect is possible when one tenant’s actions can impact others’ performance. - One app instance, several databases
In this type, a single instance of the software supports multiple databases, each assigned to a different tenant. There is no “noisy-neighbor” effect as each tenant has a separate database, and resource management is more straightforward. At the same time, the need for individual space for each tenant may lead to lower scalability and higher expenses to stay efficient.
Generally, multi-tenant architectures are characterized by scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of onboarding. For instance, consumer-facing applications, like Gmail, Google Drive, Dropbox, or Shopify, leverage multi-tenancy for efficient and secure service delivery and easily accessible storage. Cloud providers like AWS use the same hardware in PaaS, IaaS, and serverless solutions for multiple customers, optimizing resource utilization. However, they may involve trade-offs in terms of customization and potential security contemplations.
Choosing between single-tenant and multi-tenant environments depends on budget, customization needs, and data sensitivity influence.
Multi-tenant vs single-tenant cloud computing
Multi-tenant cloud security considerations
Companies can enhance the security posture of their multi-tenant cloud environments and mitigate potential risks associated with shared infrastructure when governing the following considerations:
- Ensure robust mechanisms for isolating data between tenants to prevent unauthorized access or leakage.
- Implement granular access controls to regulate user permissions and restrict access to sensitive data based on roles and responsibilities.
- Employ robust encryption protocols for data in transit and at rest to protect information from interception or unauthorized access.
- Adhere to industry-specific compliance standards and regulations to meet legal requirements and ensure data protection.
- Strengthen identity verification and authentication processes to prevent unauthorized access and protect against identity-related attacks.
- Implement continuous monitoring and auditing tools to track user activities, detect anomalies, and respond promptly to potential security incidents.
- Keep software and systems up-to-date with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities and minimize the risk of exploitation.
- Evaluate and ensure cloud service providers implement robust security measures and adhere to industry best practices.
- Implement network security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor and control traffic within the multi-tenant environment.
- Be mindful of data residency requirements and legal jurisdictions to ensure compliance and data sovereignty.
- Educate users on security best practices, including password management, phishing awareness, and social engineering prevention.

Multi-tenant LMS platform we delivered
Implement Multi Tenancy in Your Business Cloud Computing with Our Help
Transform your business activities with our expertise in custom software development. At Academy Smart, we specialize in creating secure and tailored cloud-based solutions that meet your specific needs.
With a keen understanding of cloud migration, our team ensures a smooth transition to public or hybrid clouds. We prioritize robust security measures to protect your data and applications during the entire process. Our outstaffing IT agency offers skilled professionals who seamlessly integrate into your team, enhancing your ability to manage and secure your multi-tenant cloud applications effectively.
Get in touch for a solid and resilient foundation for your online business.
Frequently Asked Questions: Cloud Computing Multi-Tenancy
What is a cloud tenant?
A cloud tenant exploits the services and resources provided by a cloud service supplier, such as computing power, storage, and applications, within a shared cloud infrastructure.
What is multi-tenancy in cloud computing?
Multi-tenancy in cloud computing is an architecture where multiple users, called tenants, share the same physical or virtual infrastructure, applications, and resources while maintaining data and workload logical isolation.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!