How to Build Human Resource Management Software Application
Contents
Amidst the prevailing trend of digitizing business processes, companies increasingly recognize the need to transition from traditional paper HR management to digital. This choice allows businesses to simplify administration, automate repetitive tasks, and more efficiently use available labor resources, reducing the cost of their management.
However, even the current saturation of the market with ready-in-box solutions does not always permit enterprises to find tools that can satisfy distinct needs. So, developing specialized HR management software may become a strategic decision that meets evolving challenges head-on. Learn more about the benefits, features, and types of HRIS/HRMS platforms in the article to create a practical enterprise HR app for your company.
What is HRM Software, and What Does It Do
Human resource management software is a comprehensive suite of digital applications designed to streamline and manage resources and employee-related processes throughout the worker lifecycle within an organization. Its primary purpose is to enhance the efficiency of HR operations, ensure compliance with changing labor laws and tax regulations, and provide valuable insights into workforce management.
In the most general sense, the entire variety of electronic HR tools is typically divided into Human Resources Management Systems (HRMS) and Human Resources Information Systems (HRIS). Both refer to software platforms that handle employee information and automate HR processes. While HRIS may primarily track numerical data and employee information, a HRMS includes non-quantitative information, such as employee satisfaction, job performance, analytics, and more.
As more complex and feature-rich, the HRMS application usually serves as a central hub for HR professionals and other stakeholders within a company to access, record, and process essential HR data. It encompasses a wide range of functionalities, including candidate recruitment, payroll management, leave approval, succession planning, attendance tracking, career progression, performance reviews, and the overall maintenance of employee records. Such human resources software is widely used today because it significantly enhances the operational efficiency of business and ensures HR industry adherence. Academy Smart’s video presentation demonstrates several examples of practical corporate applications below.
Key Features of Human Resource Management Software
Various HR applications provide multiple features that enable HR specialists to efficiently manage processes, improve workforce management, confirm compliance, and support strategic HR initiatives. The particular functionalities of employee management software required may vary depending on the enterprise’s size, industry, and HR needs, but the most common HRMS feature list usually includes the following:
- User-friendly interface
HR portal software offers a convenient online interface with employee and manager self-service options, supporting mobile apps, localization, personalized dashboards, workflow automation tools, role-based access controls, and notifications. - Centralized employee records
People management software provides a single repository for storing, updating, and maintaining employee records, improving reporting accuracy and compliance management. - Workforce planning
HR employee management software helps plan and budget for workforce costs, measures actual expenditures against budget for current and future scenarios, identifies skill gaps, and creates succession plans. - Payroll management
HRMS products accurately calculate earnings, deductions, and taxes, manage benefit elections and employer/employee costs, automate tax filing and deposits. - Recruitment and applicant tracking
HR software tools manage job requisitions, descriptions, and postings, track applicants through recruiting, and facilitate background checks and pre-employment screenings. - Performance evaluation and management
HR administration software provides tools for setting goals, evaluating employee performance, competency assessments, workflow efficiency reviews, and feedback. - Time and attendance tracking
Personnel management software processes track employee schedules, attendance, and time-off requests, integrating with payroll and project management for seamless workforce management. - Benefits administration
All-in-one HR platform helps configure benefit plans and eligibility rules, facilitating open enrollment and integrating benefit costs with accounting. - Employee engagement
Human resource software applications enhance employee engagement through features like recognition programs, career development, and mentorship opportunities. - Employee self-service
HR admin software empowers employees to update personal information, request time off, access pay stubs, and perform other HR-related tasks. - Learning management
HR apps can administer training programs and courses, track employee skill development and certifications, and control compliance training and certifications. Often, enterprises integrate HRMS platforms with corporate Learning Management Systems for direct data exchange between them. - Reporting and analytics
Human resources platforms provide ad-hoc reporting capabilities, developing key performance indicators for HR process performance, integrating HR metrics into financial dashboards for company-wide analysis and decision-making, and generating operational reports to track HR data.
Trends in the Development of HR Employee Management Systems
The evolution of corporate HR software is shaped by several noteworthy trends driving this field’s development.
One popular direction today is the integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning into HRMS applications. AI and ML technologies enhance various aspects of HR, including recruitment, talent management, and predictive analytics. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants simplify employee self-service and support, while predictive analytics is aiding in workforce planning and identifying potential employee turnover.
Another major trend is the adoption of Cloud Computing in human resources software. Cloud-based HR systems are gaining popularity due to their scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. HR management SaaS solutions allow remote access to HR data, storage, and seamless updates without needing on-premise infrastructure.
The mobile revolution is also influencing HRMS development. Mobile-friendly HRMS applications enable employees and managers to access HR-related tasks on smartphones and tablets. These apps facilitate on-the-go approvals, time tracking, and communication with HR, making HR processes more convenient and accessible.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on integrated HR suites. These HRMS products offer comprehensive modules for core HR functions, payroll, talent management, and more. The integration of these modules streamlines data sharing, enhances data accuracy, and provides a unified view of HR processes.
These trends collectively reflect the ongoing efforts to make HRMS more efficient, helpful, and adaptable to the evolving needs of business and their workforce. Embracing them can help companies improve their HR management and gain a competitive advantage of an advanced organization. Our portfolio contains examples of custom enterprise software that was created, considering the latest tendencies in the areas mentioned.

Projects delivered by Academy Smart
What Benefits May Bring Business HR Software Systems
The high demand for Human Resource Management Systems software indicates these digital platforms’ high value for the full functioning of modern business. Among the many benefits of implementing human resources apps, the most notable are the following:
- Enhanced HR data access and management
HRMS acts as a centralized storage for all employee-related data. That eliminates the problem of scattered information and simplifies data retrieval. Moreover, it introduces mobility by allowing personnel to access essential data remotely. The adaptability of HR management platforms allows customization to meet any company’s unique requirements. - Routine automation
A significant advantage of human resources manager software is task automation. It revolutionizes recruitment processes by automating job postings and candidate screening, making hiring faster and more efficient. It also handles payroll, tax reporting, and compliance checks precisely, reducing potential costly errors. Time tracking and workflow automation are additional features that optimize entire efficiency. - Advanced analytics and reporting
The best HR apps empower businesses with beneficial data-driven insights. By leveraging detailed analytics, organizations gain a deeper understanding of workforce dynamics, performance metrics, and employee engagement levels. These systems support talent development through personalized training plans and mentorship initiatives, aiding in nurturing employee potential. Furthermore, they assist in identifying high-performing individuals and addressing any productivity issues proactively. Compliance monitoring is another vital aspect where human capital management tools ensure adherence to labor laws and regulations. - Cost reduction
Common HR software promotes cost efficiency in multiple ways. It reduces the reliance on paper-based operations, leading to savings on materials and storage space. Automating tasks minimizes the need for manual intervention, optimizing resource allocation. Furthermore, the system significantly lowers the risk of costly errors, particularly in areas like payroll and compliance. By helping businesses comply with regulations, internal HR systems can potentially prevent fines and penalties. - Profitable investment
In essence, HRMS implementation delivers long-term profitability. It streamlines daily operations, allowing the HR department to allocate more time to strategic activities that enhance productivity. Access to comprehensive HR analytics and efficient workforce management gives businesses a competitive edge in the market. Ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations through HRMS safeguards the organization’s reputation.
While an initial investment is involved, the efficiency gains, competitive advantages, and long-term savings make HRMS development worthwhile and profitable for growing businesses.
HR Software Application Types with Examples Used by Companies
Applications for HR managers come in various types, each serving distinct functions within human resources administration. A company’s unique needs and priorities define approaches to choosing the right HR software set. To avoid excessive detail, we’d like to note that in the most general form, Human Resource Management System software can be divided into:
- Core HR applications
These platforms are foundational for managing essential employee data and administrative processes. They include features for personnel tracking, benefits administration, payroll management, and compliance with labor laws. A typical example of such HR employee software is BambooHR. - Talent acquisition and management systems
Human resource database software like Workable focuses on recruiting and developing talent. It encompasses applicant tracking, candidate sourcing, onboarding, and skills development. HR recruitment apps help businesses attract, nurture, and retain the top experts they need. - Workforce HR management solutions
Personnel software such as Kronos Workforce Central offers tools for efficient day-to-day HR operations. They cover time and attendance tracking, labor cost management, work scheduling, and compliance reporting. - Learning and performance systems
Software for human resource management often has abilities to facilitate employee development and productivity. They include features for assigning courses, tracking progress, conducting performance evaluations, and providing feedback. These HRMS platforms, for instance, Cornerstone OnDemand, promote ongoing learning and goal achievement.
HRMS applications are deployed using different methods to meet the diverse needs of organizations. These deployment types include on-premise, web-based, and cloud-based solutions.
- On-premise HRMS
On-premise human resource software applications are installed and maintained locally within an enterprise’s infrastructure. The organization purchases the necessary hardware and software licenses, sets up servers, and manages ongoing maintenance and updates. On-premise solutions provide high control and data security, making them suitable for companies with stringent data privacy requirements. However, they can be costly to implement and may require dedicated IT resources for maintenance. - Web-based HR systems
Web-based HRMS, or hosted HR software, is a solution where the application is hosted on a third-party server and accessed through a web browser. Organizations subscribe to these services and access their HRMS over the Internet. Web-based HRMS offers greater flexibility and scalability compared to on-premise solutions. It reduces the burden of IT infrastructure management, as the vendor handles server maintenance and updates. Users can access the online HR platform from anywhere with an internet connection, making it suitable for remote work scenarios. - Cloud-based human resources software
HR cloud system is a subset of web-based solutions, where the software and data are hosted on the vendor’s cloud infrastructure as SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) applications. This type of deployment is known for its ease of implementation and scalability. The cloud service provider usually maintains a standard feature set of the HR app, its data security, and compliance, alleviating many concerns associated with data protection. Cloud-based HR management platform offers automatic updates, ensuring that organizations always have access to the latest tools and security enhancements.
Of course, each deployment type has its advantages and considerations, and companies choose the one that best aligns with their specific needs, budget, and IT capabilities.
Finally, today the HRMS market offers various possibilities, from open-source and simple HR software for free to complex all-in-one HR systems to buy. However, if existing solutions cannot meet the enterprise’s specific preferences, you can order customized HR software development to satisfy all your challenges.
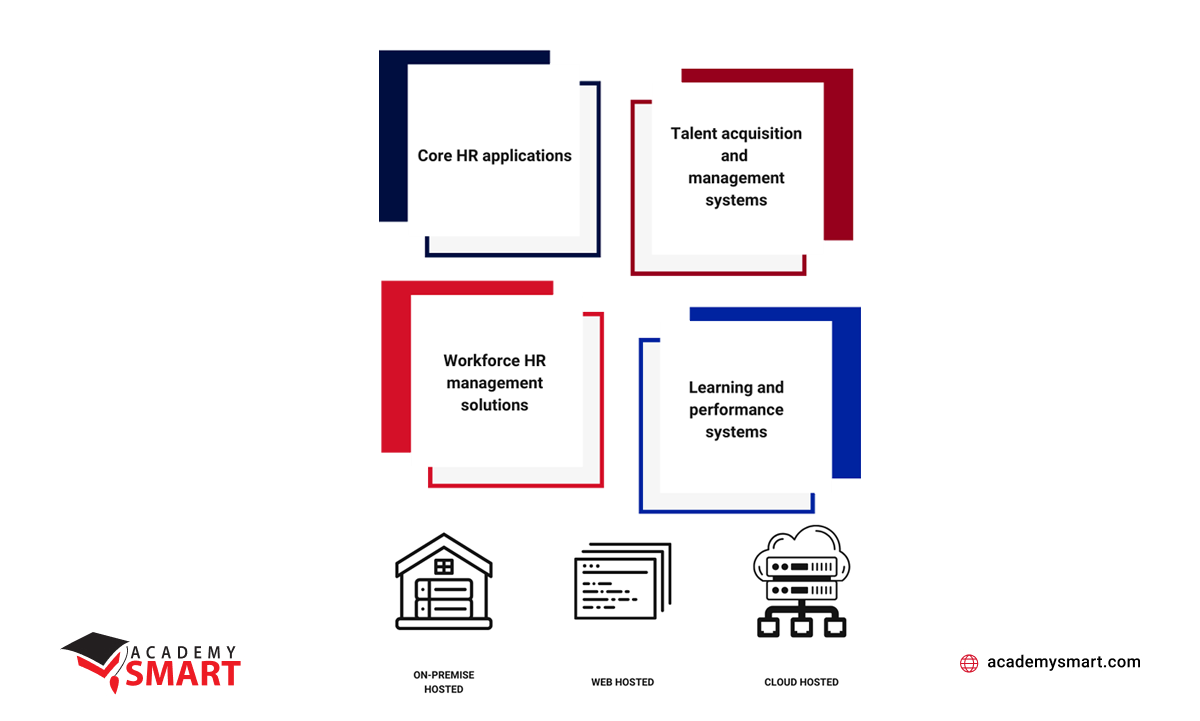
Main types of human resource application software
How to Develop HR Management Applications: Simple 5-Step Guide
The decision to create your HR application stems from several compelling reasons. First and foremost, it allows you to tailor the HRMS software to your unique organizational needs, ensuring that it aligns perfectly with the HR processes of your enterprise. Moreover, a custom solution can address industry-specific intricacies more effectively than off-the-shelf alternatives. At last, intellectual property for a comprehensive or specialized solution in personnel management makes it possible to sell licenses for the use of this product. If it successfully enters the market, this will provide an additional source of profit for the company’s owners.
Step 1. Requirements gathering and analysis
The foremost stage in developing a custom human resource management software is the meticulous analysis of the company’s demands and gathering requirements. The entire project’s success largely hinges on how well we identify and understand the critical elements and business challenges that must be considered.
The central point is a deep dive into understanding the stakeholders involved, such as HR professionals, departmental managers, and end-users. Each stakeholder group has distinct roles and expectations, making it imperative to define their specific requirements and how they interact with the HRMS. A holistic comprehension of the existing HR processes is indispensable. That involves mapping workflows, identifying pain points, and recognizing areas where automation can significantly improve. Analyzing how data flows within these processes and where bottlenecks exist is vital.
The essence of different HR systems is data. It is crucial to analyze the types of data being managed, their sources, and their destinations. Additionally, the security and privacy requirements must be detailed and examined to ensure compliance with industry standards.
The usability of the HRMS platform is critical for user adoption and productivity. Analyzing the user experience, designing an intuitive interface for various devices, and ensuring that the app HR aligns with the way users work is imperative. For seamless human resource process management, analyzing integration needs with other software systems already in place within the organization is also necessary. They may include payroll systems, time and attendance trackers, and other HR-related software. Understanding how data will flow between them is paramount.
Setting performance benchmarks and analyzing how the HRMS will handle various load scenarios is crucial. The system should deliver the required performance even during peak usage periods. Moreover, you have to consider future growth and scalability possibilities to design HRMS without requiring an urgent and complete remake later.
By strongly underlying these critical nuances during the requirement-gathering phase, we pave the way for choosing the suitable technical platform basement, tools, and efficient custom HR software development.
Finally, to successfully develop an HRMS application, you need a reliable team with the expertise to match the project’s technical specifications. At this stage, you should decide on its composition and search for the missing IT specialists or utilize staff augmentation services by agreeing with third-party IT providers.
Step 2. System design and architecture
This stage lays the foundation for the entire system, dictating its functionality, scalability, and long-term viability.
HRMS systems should be designed with a modular structure. It allows for easy scalability as your organization grows. Various modules can encompass HR onboarding apps, tracking systems, performance management, planning software tools, and more. Ensure that they are not only scalable but also interoperable.
The user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) should be at the forefront of your design. Tailor it to align with the unique needs of HR professionals, ensuring that it is intuitive, efficient, and capable of handling complex HR tasks seamlessly. Consider the design’s responsiveness to different devices and mobile platforms. Ensure you provide user training and support as part of your system design. Even the most sophisticated HRMS is ineffective if users do not know how to leverage its capabilities fully.
Decide whether your HRMS will be cloud-based, on-premises, or a hybrid. Each option has its pros and cons. Cloud solutions offer scalability and accessibility, while on-premises solutions provide greater control over data and security.
HRMS seldom operates in isolation. It must seamlessly integrate with other systems, such as payroll, e-learning, and HR job applications. APIs and middleware play a crucial role in enabling these integrations. Ensure that your architecture is designed to accommodate these connections.
To test your initial ideas, create a prototype of your HRMS application. It will help you provide a visual and interactive representation of the concept, allowing stakeholders, including HR professionals, management, and developers, to understand the proposed system’s functionality and interface. The feedback will validate HR app design, clarify tech requirements, and minimize misalignments.
Step 3. Software development
Initiate development using agile methodologies, ensuring flexibility and regular stakeholder engagement. Assemble a full-stack development team capable of handling front-end and back-end tasks cohesively. Maintain detailed documentation and ensure compliance with industry constraints.
Plan for smooth data migration if transitioning from an existing HR system is needed. Create a scalable database structure to manage employee data while complying with privacy regulations. Focus on programming server-side logic to create the core features of the application as defined in the prioritized HR software functionality list. Utilize API integrations with third-party systems for data consistency seamlessly. Enforce strict security measures, including access controls and encryption, to protect sensitive HR data.
Pay attention to user experience and create an intuitive, user-friendly HRMS interface. Ensure mobile compatibility to support remote HR tasks on various devices and platforms.
Step 4. Testing and deployment
The team diligently tests the code performance of the HR application at all development stages, identifying and addressing any bugs, errors, or issues that may have arisen. User acceptance testing is conducted to ensure that the system meets the expectations and requirements of the end-users. This step validates that the software for human resource management aligns with the common goals and preferences.
The team also develops a detailed deployment plan outlining the precise steps and procedures for implementing the HRMS apps in the enterprise digital environment. It serves as a roadmap, ensuring the transition from development to deployment is executed seamlessly. The team formulates a data migration strategy if data migration from existing systems is necessary. This approach ensures that all relevant data is smoothly transferred to the new HR management platform, maintaining data integrity and accuracy.
Comprehensive documentation is another essential deliverable. It delves into the system’s architecture, features, and user guides. It acts as a reference point for users and administrators alike, aiding them in understanding and maximizing the capabilities of the HRMS.
Step 5. Maintenance and support
When human resource management software is released, the focus shifts to ensuring the HRMS’s continued functionality, security, and optimization. This phase involves ongoing monitoring, addressing emerging issues or bugs, implementing software updates, and providing user support. It is essential for sustaining the efficiency and reliability of online HR platforms over time, adapting them to changing business needs and ensuring a positive user experience.
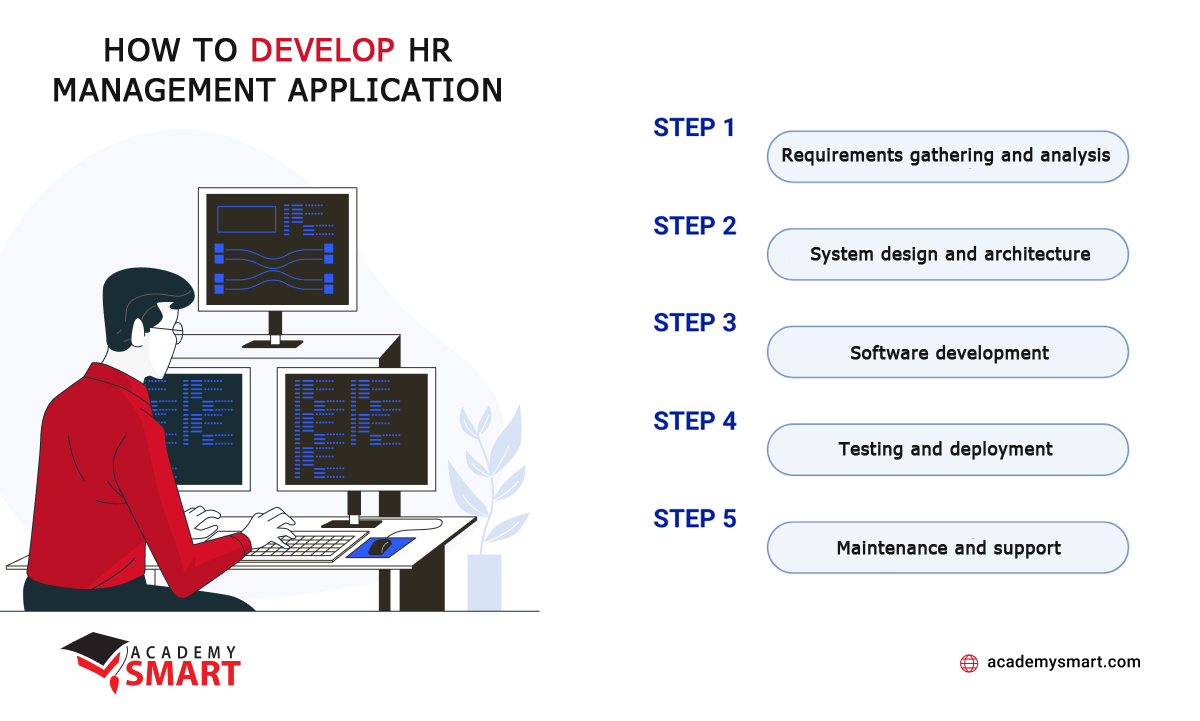
Human Resource management software development algorithm
How Academy SMART can Assist You with an Enterprise HR Software Development
As an outstaffing IT agency, we understand very well how crucial effective HR management is for large businesses. That is why the Academy Smart team invites you to use our proficiency and practical experience in developing custom online software applications to create and provide technical support for your corporate or commercial HRMS systems.
At your service are talented programmers and QA engineers, full-stack web and cloud development specialists, project managers, DevOps, and business analysts with excellent industry knowledge. Depending on your needs, we have options for IT staff augmentation and turnkey HR software development outsourcing.
Do not delay implementing good ideas, and get in touch to discuss their details.
Human Resource Management Application Development: Frequently Asked Questions
What are HR Software Application Systems?
HRMS applications are specialized software tools that streamline and automate various human resource management tasks. These systems help organizations efficiently manage their workforce, improve HR processes, and ensure compliance with labor regulations.
What are Human Resource Management Software Host Types?
Apps for HR can be hosted through different ways, including on-premise hosting, web-based hosting, and cloud-based hosting. These deployment options determine where the software for the human resource management system and its data are stored.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!