Cloud Compliance Standards: What to Consider?
Contents
Cloud compliance standards are a critical consideration for modern enterprises due to the increasing reliance on cloud services. As businesses migrate sensitive data and operations to the cloud, maintaining standards becomes imperative for data security and regulatory compliance. Failure to meet these ordinances can result in legal repercussions, data breaches, and damage to a company’s reputation. That’s why prioritizing cloud compliance ensures a robust foundation for secure and responsible business operations.
Cloud computing standards and compliance
Cloud compliance standards are the set of regulatory frameworks and industry-specific requirements that dictate how organizations must handle data in the cloud. These standards, such as SOX, ISO, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR, establish rules for protecting sensitive data, ensuring reasonable security for workloads, and undergoing regular audits. They vary across industries but generally mandate encryption, periodic security audits, and maintaining a secure environment. These standards provide a robust foundation for secure cloud solutions, emphasizing data safety and regulatory adherence.
Cloud compliance is crucial for business apps as a significant portion of corporate data resides in the cloud. Failure to comply with these standards can lead to legal challenges, fines, and data violations, with the average cost of a data breach reaching millions. The challenges lie in the evolving threat landscape, the complexity of compliance requirements, and the need for businesses to proactively address security concerns. However, considering the potential negative ramifications, neglecting cloud compliance is not an option.
Implementing cloud compliance standards in software development is a responsibility both of the cloud service provider (CSP) and the customer. Major CSPs, like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, operate under a shared responsibility model. The cloud service vendor is responsible for the “security of the cloud,” encompassing infrastructure, hardware, and physical security. On the other hand, the business is accountable for the “security in the cloud,” managing the guest operating system, application software, and configuration. This collaborative approach ensures a comprehensive strategy for maintaining compliance, with both parties contributing to a secure and compliant cloud environment.
Typical cloud compliance standards consist of the following components:
- Governance involves preset controls to oversee and guide the organization’s process in the cloud and establish a framework for secure cloud operations, ensuring adherence to business goals and regulatory requirements.
- Change control addresses challenges related to the speed and flexibility of the cloud, focusing on controlling changes to prevent misconfigurations. It manages the complexities of change in the cloud environment, minimizing the risk of configuration errors.
- Identity and access management (IAM) involves controls frequently changing in the cloud, emphasizing continuous monitoring and best practices for secure access. It ensures the integrity of IAM controls, limits access based on business needs, and enhances overall security.
- Continuous monitoring focuses on the complexity of the cloud by continuously monitoring and logging all activities, capturing a comprehensive record of events, providing an audit trail, and verifying compliance with standards.
- Vulnerability management effectively supervises vulnerabilities by understanding environments and identifying potential risks. It plays a central role in meeting regulatory requirements by identifying and remedying susceptibilities in the cloud.
- Reporting provides current and historical proof of adherence, creating a compliance footprint. It offers tangible evidence of compliance, supporting audits and demonstrating the company’s commitment to regulatory standards.
This generic structure aligns with best practices in ensuring cloud-based systems’ security, integrity, and regulatory compliance. However, it’s important to note that specific compliance standards may introduce additional or nuanced requirements based on the nature of the industry, the type of data involved, and regional regulations.
Who develops cloud standards of industry and security compliance
Developing cloud compliance standards often involves collaborative efforts between different stakeholders. This cooperation ensures that standards are comprehensive, widely accepted, and reflect industry needs. Industry organizations, regulatory institutions, and international standards-setting associations usually develop and maintain cloud compliance standards. Here are some entities involved:
- International standards organizations
Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) play a significant role in developing international standards, including those related to cloud computing and security. ISO, for example, has developed standards like ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management systems. - Industry-specific regulatory bodies
Different industries have specific compliance requirements, and regulatory bodies associated with those industries contribute to standards development. For example, the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) develops standards like PCI DSS for securing payment card transactions. - Government regulatory agencies
Government agencies at the national and regional levels often establish and enforce compliance standards. For instance, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets standards for personal data protection. - Cloud service providers
Major cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, contribute to developing best practices and guidelines. They often align their services with established standards and work to enhance security and compliance features. - Industry associations
Various industry associations and consortia may also play a role in developing particular standards. These organizations bring together experts from different companies to collaborate on best practices. An example is the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), which promotes best practices for securing cloud computing.
Essential cloud compliance solutions for your enterprise
Here’s an overview of critical frameworks that play an indispensable role in shaping cloud compliance strategies:
- ISO/IEC 27001:2013
ISO stands out as one of the most widely accepted cloud guidelines, providing a comprehensive framework for managing information security throughout its lifecycle. ISO/IEC 27001:2013, a prominent standard within the ISO family, outlines requirements for establishing and maintaining information security management systems. It ensures a robust approach to addressing security risks for cloud users and vendors. - Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA)
FISMA governs the security practices of entities within the US Federal Government, ensuring the creation, implementation, and annual review of internal security plans. It extends its purview to cover technology security in third-party organizations, including cloud vendors. - Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP)
Initiated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), FedRAMP enhances cloud security by evaluating and managing various cloud solutions and products. This program ensures that cloud service vendors comply with established security controls, providing an added layer of assurance for those operating in the federal space. - Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX)
SOX, applicable to all public companies in the US, aims to mitigate fraudulent accounting and financial activities. It safeguards the public from corporate wrongdoing, requiring companies to adhere to auditing guidelines, particularly SSAE 16 or SAS 70, when working with cloud providers. - Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Established by major credit card companies, PCI DSS focuses on securing card payment transactions. The standard includes specific requirements for protecting cardholder data, emphasizing data encryption and security measures tailored to the dynamic nature of the cloud. - General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Designed by the European Union, GDPR focuses on rectifying security compliance challenges within the cloud environment. It governs organizations working with EU residents’ information, granting individuals greater control over their data and establishing an international standard for business. - Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA, applicable within the United States, sets stringent standards for securing and managing protected health information (PHI). Healthcare entities, including hospitals, insurance organizations and various healthcare software applications, must adhere to HIPAA regulations, enhancing the security of medical data and reporting any security breaches.
In addition to these specific regulations, companies often rely on common cloud compliance frameworks such as the Cloud Security Alliance Controls Matrix (CCM), ISO 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and CIS Controls. These frameworks provide foundational regulations to improve cloud security, from protection controls to risk management practices, and help to create safe and attractive cloud applications like those in our portfolio.
Assessing Cloud Service Providers for Compliance
Efficient cloud compliance is imperative for safeguarding sensitive data, steering clear of legal entanglements, and fostering trust among clients and investors. Here’s a step-by-step guide to navigating the evaluation process:
- Begin by identifying the array of rules and industry standards governing cloud compliance. Recognize the significance of frameworks such as ISO, HIPAA, GDPR, FedRAMP, SOX, PCI DSS, and FISMA.
- Utilize the shared responsibility model, acknowledging your obligation for both the data stored in the cloud and the secure configuration of the services in use. This awareness forms the basis for clearly delineating roles between you and your cloud provider.
- Delve into the nuances of your chosen cloud environment’s service and deployment models. Each configuration impacts security responsibilities, whether it’s SaaS, IaaS, or PaaS, coupled with deployment models like hybrid, public, or private. Tailor your evaluation to the specific demands of your cloud deployment.
- Forge policies for access control that limit and authenticate admission to your cloud environment and its stored data. Introduce measures such as expiration dates and need-based access rules to maintain a meticulous record of who accesses your data and for how long.
- Assume data classification as a best practice, sorting them into categories to facilitate effective management and secure storage. Reserve internal networks for highly confidential or sensitive data, ensuring a prudent approach to migrating data to the cloud.
- Prioritize encryption as a fundamental strategy for protecting sensitive data at rest and in transit. Encryption fortifies your data against potential breaches and aligns with compliance requirements such as GDPR and PCI DSS.
- Institute internal security audits to uncover vulnerabilities and ensure ongoing alignment with regulatory requirements. These audits serve as a proactive measure to identify and rectify security gaps.
- Develop a thorough understanding of SLAs and legal contracts with your cloud service provider. That comprehends ground rules, expectations, and the commitments outlined in the contractual agreements.
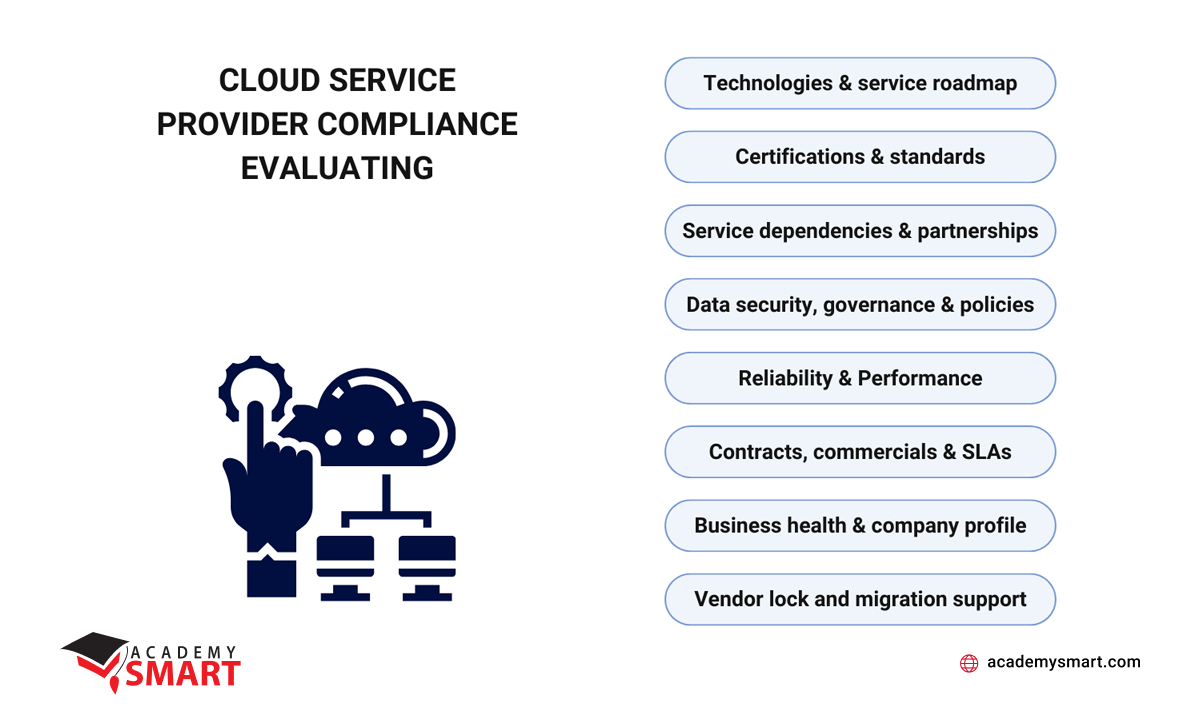
What is essential to consider in evaluating cloud service providers when your enterprise plans to comply with regulations in cloud security and industry-specific requirements?
- Technologies & service roadmap
Assess the provider’s technology roadmap, evaluating its alignment with your company’s future needs and ensuring a commitment to evolving technologies. - Certifications & standards
Scrutinize the provider’s certifications and adherence to relevant compliance standards, validating its commitment to meeting industry benchmarks. - Service dependencies & partnerships
Understand the provider’s dependencies and partnerships, as these can impact the reliability and security of the services offered. - Data security, governance & policies
Evaluate the provider’s approach to data security, governance, and adherence to business policies, ensuring alignment with your corporate objectives. - Reliability & performance
Gauge the provider’s track record for reliability and performance, considering uptime and adherence to service-level commitments. - Contracts, commercials & SLAs
Review contracts, commercials, and SLAs to ensure transparency and alignment with your enterprise’s operational and financial requirements. - Business health & company profile
Examine the provider’s financial health and overall profile, assessing stability and long-term viability. - Vendor lock and migration support
Assess the provider’s support for migration and exit planning to avoid vendor lock-in and ensure a seamless transition when needed.
By systematically navigating these steps, companies can establish a robust framework for cloud compliance, mitigate risks, and strengthen the foundation for secure cloud operations.
Using cloud well-architected frameworks for compliance assurance
Well-architected cloud frameworks provided by leading cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are invaluable best practice guidelines for cloud engineers. They systematically address key pillars of operational efficiency, security, and cost-value considerations, offering a reliable pathway to achieving compliance objectives.
AWS’s well-architected framework provides comprehensive policies for architects designing workloads and applications in the Amazon cloud. It revolves around questions facilitating the critique of cloud environments, serving as a robust resource for architecture evaluation. Amazon developers are guided by five fundamental principles — operational excellence, security, reliability, performance efficiency, and cost optimization.
Microsoft Azure offers a set of guiding tenets to improve the quality of cloud workloads. Comprising five pillars — reliability, security, cost optimization, operational excellence, and performance efficiency — it enables practitioners to develop high-quality, stable, and efficient cloud architectures. Supported by elements like the Azure Well-Architected Review and Azure Advisor, this framework provides actionable insights aligned with the key pillars.
Google’s framework provides a foundational approach to constructing and enhancing cloud offerings. Emphasizing four main principles — operational excellence, security and compliance, reliability, and performance cost optimization — it instructs engineers in designing secure, efficient, resilient, and cost-effective cloud topologies.
While adopting multiple cloud compliance standards may be necessary, these frameworks offer a streamlined approach, reducing effort through meticulous planning and execution. External expertise may be sought to optimize and structure cloud compliance strategies tailored to the business’s unique requirements, size, and industry focus.
How to analyze compliance of the cloud solution to the standards and best-practices
Ensure Cloud Compliance with Our Team Assistance
With over 14 years of experience, Academy Smart assists clients in smoothly integrating cloud technologies into their enterprise operations. Our services include consulting and cloud migration, developing native cloud applications, and engineering hybrid and multi-cloud solutions using Amazon AWS and Microsoft Azure.
Our team comprises highly skilled professionals with expertise in programming microservices, containerization, cloud infrastructure deployment, and management. Whether you’re looking to strengthen your in-house workforce with top talent or assemble a dedicated development team for a project, we’re here to help.
Contact us to turn ideas into practical solutions if you’re considering improving your business cloud computing compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions: Cloud Relevant Compliance Standards
What are the key cloud compliance standards I should be aware of?
Prominent cloud compliance standards include:
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
- SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2)
- ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System)
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
How can my business assess its cloud compliance readiness?
Companies should conduct cloud compliance examinations to evaluate their current state of adherence, identify gaps, and develop remediation plans.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!