Cloud Computing and Distributed Systems as Resources for Business Growth
Contents
In the dynamic evolution of computer network technologies over the last two decades, the emergence of transformative computing models, notably distributed computing and cloud computing, has been profound. Despite distinct terminologies, the essence remains consistent. To comprehend cloud computing entirely, delving into distributed systems and their departure from traditional centralized computing is essential. This article unveils the nuanced distinctions between cloud and distributed computing, highlighting their pivotal roles as indispensable resources for the digital transformation of modern enterprise.
Definitions of Cloud and Distributed Computing
What is distributed computing
Distributed computing is a computational model where tasks are divided and processed across multiple interconnected computers, fostering parallel processing and collaboration. Unlike traditional centralized computing, this approach harnesses the collective power of a network, allowing for efficient problem-solving and resource utilization.
The advantages of distributed computing are:
- Parallel processing
Distributing tasks among multiple computers enables parallel processing, significantly reducing processing time for complex problems. - Scalability
The system can quickly scale by adding more nodes, accommodating increased workloads without compromising performance. - Fault tolerance
Distributed systems exhibit robustness against individual node failures, ensuring continuous operation despite hardware issues. - Resource efficiency
Practical usage of resources across the network enhances overall system performance and responsiveness.
The main types of distributed computing are:
- Cluster computing
It involves connecting multiple computers (nodes) to work as a single system, sharing processing tasks and resources. - Grid computing
Utilizes a network of geographically dispersed computers to work on a common task, often used for large-scale scientific or research projects. - Parallel computing
It involves breaking down a large task into smaller subtasks that multiple processors can process simultaneously, optimizing computational speed. - Peer-to-Peer computing
It enables individual computers (peers) to share resources and processing power directly, creating a decentralized network.
Examples of distributed computing include:
- SETI@home utilizes volunteers’ idle computer processing power to analyze radio signals from space in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence.
- Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework for distributed storage and processing large data sets, widely used in big data analytics.
- BOINC (Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing) supports various scientific research projects by harnessing idle computing resources from volunteers.
- Google File System (GFS) enables distributed storage of large amounts of data across multiple servers.
What is cloud computing
Cloud computing is a paradigm that supplies online admission to a shared pool of computing assistance over the Web. It encompasses services like storage, processing power, and applications, allowing users to leverage computing capabilities without needing local infrastructure.
The benefits of cloud computing are:
- Cost efficiency
Users pay for resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, reducing upfront costs and allowing for more efficient budgeting. - Managed services
Cloud providers handle maintenance and updates, relieving users of the burden of infrastructure management. - Scalability
Cloud services offer seamless scalability, enabling users to increase or decrease resources based on demand. - Accessibility
Users can access services and data from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering remote collaboration and flexibility.
The main types of cloud computing are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources over the Web, including storage, processing power, and networking.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) allows users to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with infrastructure complexities.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers various software applications over the Internet, eliminating the necessity for local installations.
- Function as a Service (FaaS), or serverless computing, allows developers to execute individual processes in response to specific events without managing the underlying infrastructure.
Famous examples of cloud computing services include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
It contains a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including computing power, storage, databases, machine learning, and more. - Microsoft Azure
A cloud computing platform provides virtual computing, analytics, storage, and networking services. - Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google’s cloud services encompass computing, storage, databases, machine learning, and data analytics. - IBM Cloud Functions
It provides a serverless computing environment, allowing developers to execute individual functions in response to events without managing the underlying infrastructure.
Differences between Distributed Computing vs Cloud Computing
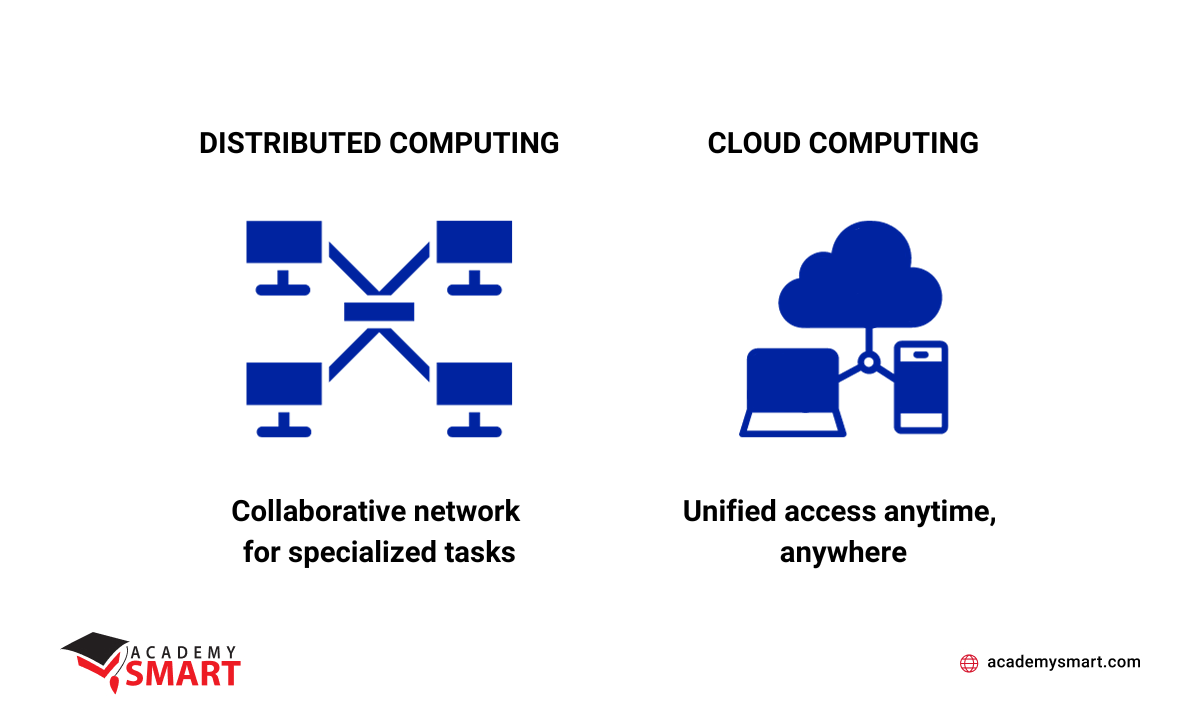
While both are rooted in extensive computer networks, distributed and cloud computing diverge in their fundamental principles and applications.
Distributed computing orchestrates tasks across interconnected machines, fostering collaboration to solve intricate problems efficiently. It can occur in closed, private, or open public networks and extend to the Internet. Its core tenets lie in resource optimization, scalability, and resilience against hardware failures.
Conversely, cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources via the Internet and outsourcing infrastructure management. Despite cloud computing being a specific implementation of distributed computing, it serves as a model for providing broader IT services than just computing.
The divergence in their focus underscores the necessity for businesses to discern these nuances, aligning their choice of computing model with the intricacies of their specific objectives.
Cloud computing and distributed systems concepts
Distributed Computing and Cloud Computing in IT Management Strategy
Distributed computing suits applied problems in scenarios where parallel processing and fault tolerance are paramount. For instance, fraud detection algorithms can leverage distributed systems to analyze vast datasets swiftly in the financial sector. In healthcare, distributed computing may aid genomic research by spreading complex calculations across multiple nodes. Additionally, industries with extensive sensor networks, like manufacturing, may benefit from distributed systems to process and respond to real-time data efficiently.
Cloud computing offers unparalleled advantages across diverse industries. In retail, dynamic scaling ensures seamless handling of fluctuating online traffic. Healthcare institutions utilize cloud services for secure data storage and collaborative research initiatives. Education leverages cloud platforms for accessible and scalable e-learning solutions. Cloud computing minimizes upfront infrastructure costs for startups, fostering rapid development and deployment. Its flexibility and cost-efficiency make cloud computing a cornerstone in crafting resilient and adaptable IT management strategies across various sectors.
Benefits of combining cloud and distributed computing
Leveraging cloud and distributed computing in tandem can offer a powerful and versatile solution for any business. Here’s why:
- Hybrid approaches for optimal performance
Combining cloud and distributed systems allows companies to create a hybrid infrastructure that capitalizes on both strengths — for instance, utilizing the cloud for scalable and elastic workloads while relying on distributed computing for performance-critical, low-latency tasks. - Data optimization
Businesses often deal with varying types of data. Cloud solutions can handle large-scale data storage and processing, while distributed systems can be fine-tuned for specific data-intensive tasks. Integrating both allows for optimized data management. - Risk mitigation and business continuity
Relying on a single approach can be risky. Cloud outages or disruptions in a distributed system can occur. A combination ensures that if one part faces issues, the other can pick up the slack, enhancing overall system resilience and ensuring business continuity. - Integration with existing infrastructure
Many companies have legacy systems in place. Merging cloud and distributed solutions permits a smoother transition, ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure while exploiting the benefits of modern technologies. - Scalability and flexibility
Cloud computing provides unmatched scalability, making it perfect for handling variable workloads. Meanwhile, distributed computing can offer a more fixed, robust infrastructure. Together, they deliver the flexibility needed to scale up and down efficiently while maintaining a solid foundation. - Cost-efficiency and control
The pay-as-you-go model of cloud computing can be cost-effective for specific tasks. However, distributed computing can offer more control over costs for consistent workloads or specific performance demands. By strategically converging the two, businesses can balance their budgeting. - Adaptation to changing needs
Business needs to evolve. The compound approach allows for adaptation to changing requirements. As an enterprise grows, it can scale up its cloud usage. If there’s a need for more governance or specific optimizations, distributed computing components can be introduced or modified accordingly.
The synergy between these approaches can create a robust, adaptable, and high-performing IT infrastructure tailored to the unique needs of a business. For example, HousePlus, the real estate application we delivered, utilizes both distributed and cloud computing, addressing many industry challenges at the most advanced level.

An excellent example of the convergence of distributed and cloud computing in one app
Increase Your IT Potential with the Academy Smart’s Team
Our team has been assisting clients in creating and implementing complex enterprise applications across various business sectors for over 13 years. Our most sought-after services include:
- outsourcing custom software development;
- cloud migration support;
- outstaffing of qualified professionals such as programmers, cloud infrastructure engineers, DevOps specialists, business analysts, and IT project managers.
Feel free to get in touch for expert advice and the development of high-performance IT solutions that propel your business forward.
Frequently Asked Questions: Cloud Computing vs Distributed Computing
What is the fundamental difference between cloud and distributed computing?
Cloud computing involves accessing resources and services over the internet, while distributed computing refers to using a network of computers to solve a problem.
How does cost modeling differ between the two approaches?
Cloud computing often follows a pay-as-you-go model, while distributed computing may involve higher upfront costs but potentially lower long-term expenses.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!