Cloud Computing in Data Management: challenges, practices, cases, and benefits
Contents
Introduction
Let’s talk about cloud computing in data management and its benefits. The COVID-19 pandemic forced many organizations to transition to remote work, and this has become the new normal. As a result, corporate data stores are increasingly accessed and updated over the Internet from numerous locations, which poses security threats. Employees have to work on reports, presentations, text documents, audio recordings from the meetings, text documents, images and a ton of other types of data in a secure, transparent and manageable environment.
Most importantly, the data variety, velocity and volume also grow exponentially, meaning the corporate data management becomes a challenge of an ever-increasing magnitude, even if it never reaches the scope of Big Data management challenges. Many organizations decide to overcome this challenge using the cloud computing capabilities.
However, in order to use cloud data management effectively, one must be aware of the fundamentals, as well as remain on top of best practices and learn from success stories of other companies. Therefore, every organization must find the most cost-efficient way to process the exponentially increasing influx of data to make it serve the business objectives best. Read on to discover the benefits, challenges and best practices of cloud application development, data management and DevOps implementation.
What is cloud data management?
Cloud data management is essentially a practice of storing and processing the company’s data offsite, rather than with on-prem servers, using services of specialized cloud hosting providers. This grants access to purpose-built automated backup tools, professional support and many other benefits.
There is a wide range of questions every data management professional has to answer at some point:
- What is the most cost-effective and secure location to store your data?
- How many cloud or on-prem data storages does your organization need?
- Do you have access to sufficient cloud storage resources to meet all your organizational data processing needs?
- How frequent are the backups? Are they automated? For how long are they stored?
- How can your personnel access their mission-critical documents and data securely when working remotely?
This is just the tip of an iceberg, but you surely get the point. Thus, every organization has to find a way to organize its public and private cloud or on-prem data management processes. Along with a strict hierarchy and structure, cloud-based data management provides tools and cloud-native features allowing to get the most value out of your data.
Cloud-based data management technologies are a cost-effective alternative to purchasing and maintaining on-prem data centers. Instead, you rent cloud-based resources as needed, or can select a hybrid cloud modernization approach, combining the ultimate control of on-prem infrastructure with processing capabilities of the cloud.
There are several crucial steps to enabling cost-efficient cloud-based data migration, storage and processing:
- Ensure accurate visibility of cloud account resources usage
- Archive your data based on actual usage, not assumptions
- Plan data management strategies in advance and forecast savings
- Use last-accessed time instead of last-modified to avoid costly archiving errors during migration
- Make data migration processes as easy as possible and run multiple migrations in parallel to save time
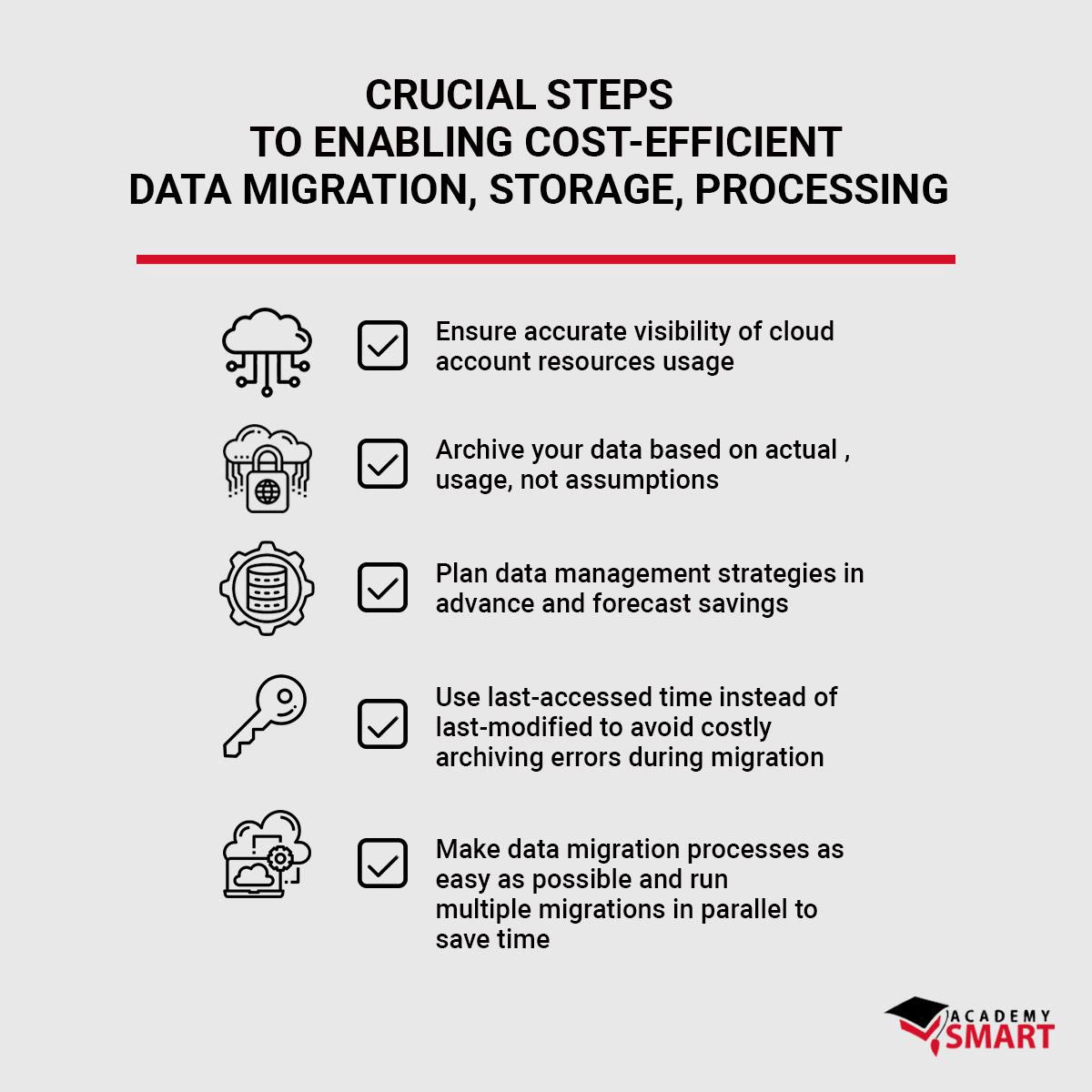
These are just the common-sense recommendations, the specifics will vary depending on your organization’s technical maturity.
How Does Cloud Data Management Differ from Traditional Data Management?
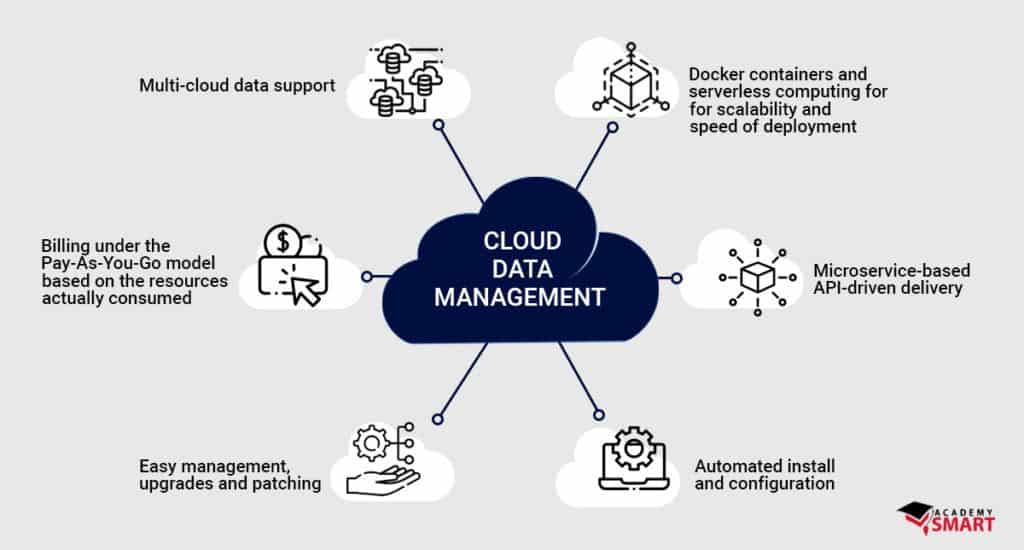
While traditional data store management platforms work well for on-prem data centers with virtualized environments like VMSphere, most of them are not built cloud-native and struggle with supporting elastic and flexible multi-cloud workloads. Therefore, building cloud-native data management tools is a great example of future-proofing and provides various benefits:
- Multi-cloud data support
- Microservice-based API-driven delivery
- Docker containers and serverless computing for scalability and speed of deployment
- Automated install and configuration
- Easy management, upgrades and patching
- Billing under the Pay-As-You-Go model based on the resources actually consumed
Thus said, cloud data management is a much more cost-efficient approach as compared to running an on-prem data center. Besides, it provides many more benefits we describe below.
Top 11 benefits of cloud data management
There are multiple advantages of DevOps cloud approach to data management, as compared to manual in-house data processing workflows:
- Cost optimization. Instead of running on-prem servers 24/7 and having to operate them in shifts even when the majority of your personnel is asleep, you benefit from lowering your Total Cost of Ownership. As you shift the major part of your expenses from CapEx to OpEx and significantly decrease the upfront investments, data management transition to the cloud helps save a ton of money in the long run.
- Improving the data processing quality. Implementing cloud infrastructure allows building automated data processing pipelines to filter out duplicate files, unneeded file versions and other outdated data that simply takes up storage and resources.
- Building a centralized cloud-based data vault. Instead of hunting for the latest file versions and most relevant data across a variety of local storages, you get everything processed with a single easy-to-manage platform.
- Reducing the IT dept toil. Instead of cataloguing all the equipment and running update trains on separate environments, your IT department can devote their time and skills to delivering value and helping your team reach business objectives — while the cloud vendor takes care of hardware maintenance and software updates.
- Scaling your systems up and down on demand. Allocate the money previously wasted on operational overhead to enable your organization to succeed faster.
- Safeguarding your mission-critical assets. Cloud deployment means leveraging the cutting edge of technology, both in terms of software and hardware. Instead of investing your stretched budget and efforts into a standalone cybersecurity solution, you can benefit from holistic protective measures offered by cloud hosting providers.
- Facilitating remote access for your staff. Ensuring your employees can have secure access to the data they need, anytime, anywhere is a great way to empower collaboration and boost productivity of your remote workforce during the pandemic.
- Ensuring data consistency and compliance. A centralized data storage and processing platform removes the hurdle of making separate data silos to interact with each other. This removes duplicate data and processes, while also allowing you to introduce and enforce compliance standards.
- Enabling business contingency and disaster recovery. Spotting the oncoming disaster, reacting to it and recovering from it are much easier in the cloud, when you have qualified monitoring, alerting, logging and support services in place. This helps reduce MTTR significantly and ensure business continuity.
- Leveraging continuous updates. As cloud data management platforms are built to work on the cutting edge of technology, they are continuously updated to ensure they support all the latest innovations. Most importantly, this happens in the background, so you do not need to reinstall and reconfigure your data processing pipelines.
- Tapping directly into the expertise pool. By working with the technical support from your cloud-based data management platform, you benefit by gaining direct access to knowledge holders who will help you get the most value out of your investments.
Cloud data management challenges & use cases
What are cloud data management challenges and benefits? There are several obstructions an IT team must overcome to ensure cost-efficient data management:
- Data storage minimization. With the ever-growing volume of data every organization has to handle, storing it long-term can incur significant expenses. Thus, every organization is bound to find the best approach for their unique operational DNA.
- Regulatory compliance. Regulators continue to update compliance frameworks in every industry, so your IT team needs tools to quickly adjust the data management processes and demonstrate compliance on request.
- Automating data management in complex environments. Whether your data resides in public, private or hybrid cloud, managing it can become a burden for your IT department. Automation helps reduce the effort needed to build error-proof streamlined data processing pipelines.
- Costs reduction. Every tool and solution in use must enable your organization to do more while spending less resources — and data management platforms are no exception.
As a result, many executives turn to cloud-based data management as the best solution.
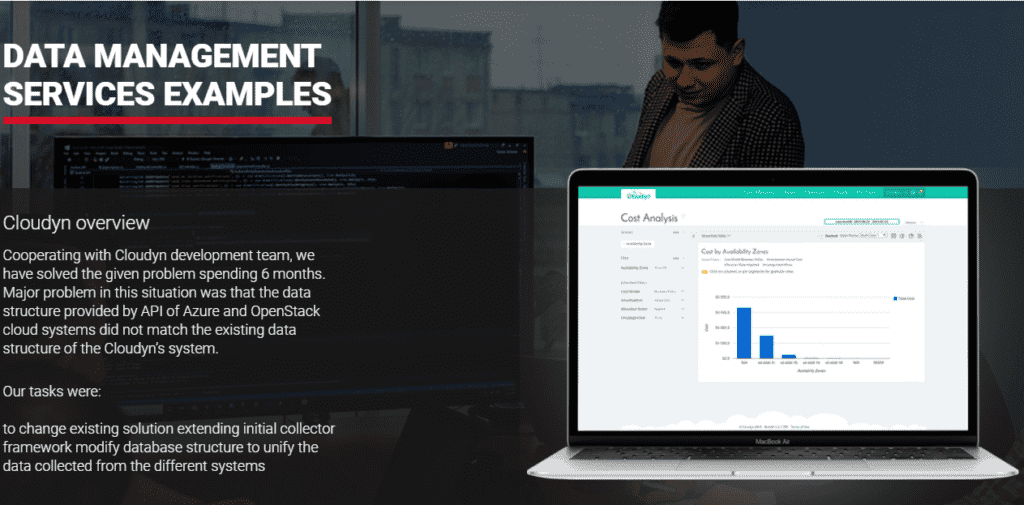
Back in 2017, Microsoft finished an acquisition of Cloudyn, a solution for in-depth monitoring and analytics of costs for AWS, Azure and other cloud platforms. The acquisition forced the Cloudyn team to seek help with organizing their server base and rearranging their cloud environments in the most rational way. The Academy Smart team helped Cloudyn achieve this goal in 6 months.
The major obstacle to restructuring these workflows was the fact that the Cloudyn API data structure in use did not match the Azure and OpenStack architecture. By closely cooperating with the Cloudyn team, Academy Smart architects were able to restructure the API and data processing mechanisms in use, so that from early 2020 all new Cloudyn features are integrated into Microsoft Azure directly.
Best practices for cloud data management strategy
What is the best strategy for cloud data management? The first step in your cloud data management journey should not be buying a tool for it. You need to design a long-term data governance strategy that aligns with your organizational needs and goals, and select the system that fits this strategy best.
Most of the readers definitely have such a strategy in place, so they just need to perform cloud modernization, namely enabling secure remote user access, implementing granular security for different data types, guaranteeing regulatory compliance and standardizing the types of data in use to minimize workflow complexity.
However, should you need to design a data management strategy from scratch, you would need to answer the following questions:
- What are the long-term business goals of your organization?
- What data do you need to handle to achieve these goals?
- What types of data do you already use?
- What data sources do you have now and plan to add in the future?
- How are you ensuring regulatory compliance now and plan to do it in the future?
- Who will have access to the data and what levels of access will there be?
- What cybersecurity controls and measures are needed to protect the data?
- How do you plan to perform disaster recovery?
- How will you collect, analyze, clean, transform and extract the data?
- How will you ensure data privacy?
- How honest and transparent do you plan to be regarding your data management?
Naturally, if there are some core principles to uphold and underwater reefs to avoid in cloud-based data management, there should be techniques that allow improving operational performance and your overall experience. Here are the most essential of them:
- Build robust and flexible infrastructure. You might need to move data from on-prem to hybrid, public, private or multi-cloud environments, and your system architecture should allow doing this without issues.
- Select a centralized cloud data management platform. Every organization’s cloud computing infrastructure becomes more complex with time. Going for centralized data management from the start helps keep the things uniformed and predictable.
- Ensure CDMI-compatibility. Cloud Data Management Interface is the industry standard increasing interoperability of various systems. Ensure your future tooling is CDMI-compatible to ease its integration with cloud components.
- Develop a policy and a framework for data management. Data migration is a complex process, so make sure your employees are aware of what they can — and cannot do with the data they manage. This will help them make conscious and informed decisions throughout the way.
Mistakes to avoid
Which mistakes in cloud data management need to be avoided? Having highlighted the four cornerstones of an efficient data migration strategy, we need to also define the biggest potential risk factors that might undermine your efforts:
- Not instating a corporate policy. Centralized data management is only possible when all departments follow the same procedures regarding collection, storage and processing of data. When the data is managed according to several separate workflows across the organization, mistakes and mismatches are inevitable. Introducing a company-wide data management policy helps minimize the number of bad decisions and data mishandling cases.
- Moving to the cloud completely. All the benefits of the cloud are available at one condition only — when there is Internet uplink. Thus, some mission-critical digital assets like domain controllers and local file servers should stay on-prem to ensure your operations are fault-tolerant.
- Keeping the data unstructured. The data must have a common structure to be organized. Classification based on proper file formats and names is quite simple and helps keep the things in order.
The future of Cloud Data Management
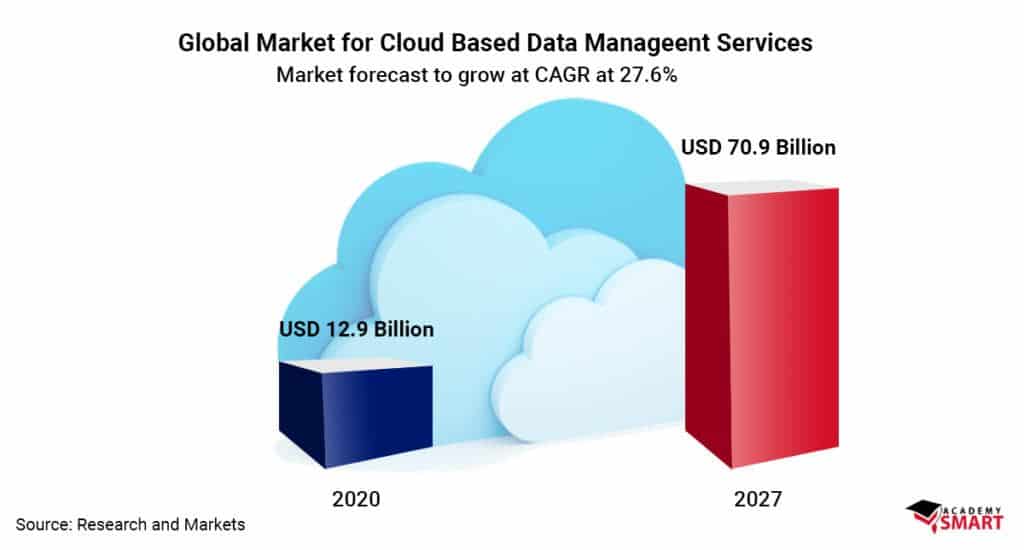
The COVID-19 pandemic boosted the demand for reliable cloud data management services. While ResearchAndMarkets estimated the size of the global data management services market to reach nearly $13 billion in 2020, the revised analysis forecasts it to grow at a CAGR of 27.6% to almost $71 billion by 2027.
Streamlined and predictable data management in the cloud is steadily replacing outdated local data storages. With the need to work remotely and save budgets, the businesses are increasingly favoring cloud deployments for their data storages. Big technology vendors like AWS, GCP and Azure offer a wide range of cloud-based data processing services and companies like Oracle deliver technology-specific solutions like Java cloud. Thus, the shift from the on-prem data storage is inevitable for any company that wants to remain competitive in its respective field.
We can highlight the following data management trends that are on the rise in 2021:
- An ever-increasing number of enterprises introduce centralized data management solutions that operate different data centers as a single entity.
- Businesses have to stay on top of their data in order to drive decisions based on numbers, instead of hunches and gut feeling.
- Organizations increasingly invest in their public, private or on-prem cloud modernization to support innovative technologies like AI and Machine Learning. This will allow discovering room for improvements in their processes and workflows.
- Corporate data is leaving the confines of on-prem data centers and migrating to the cloud to help global enterprises remain flexible and competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape.
- However, data migrations should happen only after a strategy, a framework and all the required policies are in place to guarantee data governance and regulatory compliance.
Summary
With the transition to cloud-first strategies across multiple industries, cloud data management becomes an essential part of long-term business success. However, without proper expertise you are bound to make mistakes or get very little value out of migrating your data to the cloud.
Thus said, there is no carved in stone handbook for managing the data in the cloud. It all depends on your organization’s operational maturity and current business needs. Still, knowing the best practices and avoiding hidden pitfalls can do no harm. Academy Smart can gladly lend a hand in designing and implementing cloud-native data management workflows for your business. Contact us and you will get measurable results quite soon!

Cloud computing in Data management: Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of cloud data management?
Cloud-based data is stored on servers and is accessible to you via the internet. Cloud computing is good for business.
Where can cloud computing be applied?
- Data backup.
- Disaster recovery.
- E-mail.
- Virtual desktops.
- Software development and testing.
- Big data analytics.
- Customer-facing web applications.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!