What is Cloud computing and why is it good for business?
Contents
1. Introduction
The need for cloud-based infrastructure increases steadily and is forecast to grow with a CAGR of more than 15% till 2024, surpassing 1 trillion USD in spending on cloud services globally in 2024, the IDC’s cloud forecast report states.
Cloud computing is an umbrella term referring to a business model when your data is not stored on your local on-prem servers but is stored and accessed over the Internet through the infrastructure of the cloud service providers like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure.
In short, cloud computing grants remote access to everything your business needs – servers, file storage, databases, software tools, networking, monitoring, Big Data analytics and AI/ML solutions, so you can innovate faster, have flexible resources and scale your services without investing in hardware purchase and maintenance, reducing CAPEX to zero. The Pay As You Go (PAYG) model enables you to pay only for the resources your business actually consumed, lowering your OPEX to help you run the business much more cost-efficiently.
Whenever you use some social media like Facebook or Twitter, send an email through Gmail, play some online games like World of Warcraft, watch a funny cat video on YouTube, listen to music on Spotify or do any other actions – you are using the cloud. While the first public cloud computing service was released by Amazon 15 years ago (Amazon EC2 in 2006), businesses, governments, and organizations of all kinds are just now starting to actively adopt cloud computing for a variety of reasons.
2. Types of Cloud Computing
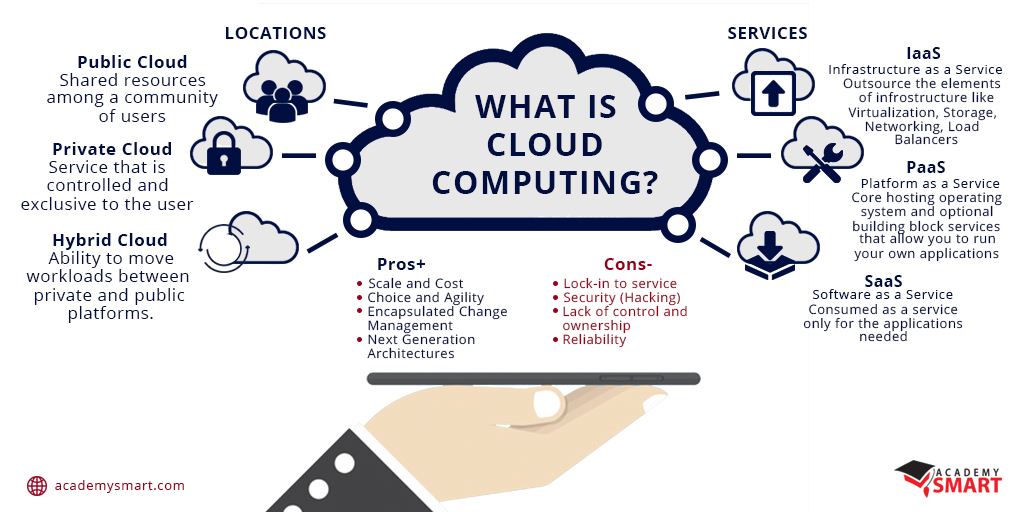
Multiple types of cloud services in cloud computing serve different purposes. Several models, location types and approaches to cloud computing are available to meet your particular requirements. The first step is to determine the best cloud deployment type for your project: public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud.
Public Cloud
Public cloud is the default offer for any business or organization that wishes to have a scalable and cost-efficient infrastructure. Computing resources like CPU power, RAM, disk space, etc. are delivered in packages called “instances” that are formed from a pool of resources available in a particular Availability Zone or region. If you need extra resources, new instances spin up in seconds. When you have no further need for these resources, extra instances are shut down to preserve your budget.
Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure Cloud Services, and Google Cloud Platform are examples of the public cloud.


Thus said, opting for public cloud can be the best choice for running a product, but this might not be the best scenario for developing it, as you will not be able to utilize the resources 24/7. In addition, as all the public cloud customers share the provider’s hardware infrastructure, data security can be a concern. However, the infinite scalability and the ability to leverage long-term-use discounts, spot instances, reserved instances, and other ways to reduce expenses make the public cloud the go-to choice for startups and SMEs.
The pandemic did not slow the growth of the public cloud sector. The US is the largest cloud computing consumer, having at least 50% of the total cloud computing market and the spending on cloud services rose from $125 billion in 2019 to nearly $150 billion in 2020.
Private Cloud
Private cloud is a sector of public cloud (usually several subnets) dedicated to serving a single organization. Protected by bastion hosts and other cloud security measures, such infrastructure is not accessible by other cloud users. This allows organizations to move their data hubs to the cloud and stop maintaining their on-prem data centers while keeping their mission-critical data secure.
In addition, such an approach enables safe remote access and user data management through password-protected private networks for geographically-distributed organizations. This is the best choice for scenarios when both scalability and security are essential – for government organizations, military entities, etc. A private cloud provides full control over the cloud resources allocated to you – only the underlying hardware is the cloud provider’s concern.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud combines the stalwart security of on-prem data centers with the scalability of the public cloud. Your mission-critical digital assets are hosted on-prem, while highly scalable customer-facing systems and workloads run in the public cloud. Two parts of your infrastructure are connected through some purpose-built solution that ensures secure and reliable operations. The global market of hybrid cloud solutions is forecast to reach nearly $130 billion by 2025.
Multi-Cloud
The main reason behind using several cloud service providers at once is avoiding vendor lock-in. This is possible because cloud vendors like AWS, IBM Cloud, Microsoft Azure, or GCP provide lots of complementary features that work well in tandem. Thus, employing a multi-cloud strategy provides flexibility in terms of cost-efficiency and infrastructure reliability, preventing any downtime and data loss. Most importantly, with tools like Terraform or Pulumi, you can create automated procedures to switch between various cloud components in no time.
3. Cloud Computing models: IaaS, PaaS, serverless, and SaaS
There are three leading models of cloud computing services delivery: Infrastructure-as-a-Service or IaaS, Platform-as-a-Service or PaaS, Software-as-a-Service or SaaS, and serverless functions. These differ based on the level of technical expertise needed to utilize them and the level of admin capabilities they provide.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The basic level of the cloud stack, IaaS infrastructure as a service cloud computing allows access to the cloud provider’s servers, networking, operating systems and object storage. Cloud users have full control over their resources and are solely responsible for monitoring them and ensuring their security.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Every of the PaaS cloud service providers delivers some services (like IBM Foundry or Google App Engine) that leave the infrastructure layer to the vendor but provide a wide range of capabilities to the users. Scalable middleware applications that are easily configured through the dashboard are the main use case for PaaS.
Serverless computing
Being a specific PaaS case, serverless functions (Amazon Lambda, Google Functions, Azure Functions, IBM Functions, etc.) provide an event-driven environment where cloud users don’t have to configure and manage their servers. They only need to upload the code and specify triggers – events, webhooks, API calls, other functions, etc. that will cause it to execute. This allows creating complex ecosystems with utmost cost-efficiency of resource usage.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
The widest cloud computing segment, where businesses rely on SaaS cloud services
from cloud providers or third-party vendors to run and manage the infrastructure and platforms, and the users only take care of the apps they upload and run online. There are multiple examples of SaaS apps, some of which run directly in the browser. For example, there is Cloudyn by Microsoft, which is a SaaS solution providing greater visibility into Azure, AWS, GCP and other public clouds resource usage and performance, supporting steady cloud growth of Cloudyn users.

4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Below we briefly overview the benefits and shortcomings of cloud computing you should be aware of.
Top benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is vastly different from traditional on-prem servers or dedicated data centers. Here are seven main advantages causing organizations to move to the cloud.
1. Cost
Cloud computing removes the main CAPEX items of on-prem data handling – building and maintaining data centers, server racks, ventilation, and humidity control systems, backup electricity lines and diesel generators, buying and replacing the server hardware and software needed to run your apps, paying wages to IT staff running all this around the clock, etc.
2. Speed
Ordering and configuring a new batch of cloud computing resources or services is as easy as clicking several checkboxes in the dashboard. You get these instances or services up and running in mere minutes. Compared to hours and days of manual on-prem server provisioning, cloud computing provides a great speed of resource allocation and configuration.
3. Global scalability
Through your cloud account dashboard you can easily add more resources – CPU power, RAM, object storage, bandwidth – or remove them as needed, thus scaling your systems up or down to meet the demand and avoid overpaying.
4. Productivity
With typical infrastructure maintenance tasks performed by cloud provider’s staff, your IT team is free from tedious chores and can concentrate on achieving business goals.
5. Performance
Leading cloud service providers run networks of secure datacenters across the globe and continuously upgrade their hardware and software to provide the latest, most performant and most secure technology available.
6. Reliability
Reliability and high-availability of cloud computing resources ensure that data backup, recovery, and continuity procedures are much cheaper and less effort-consuming.
7. Security
Cloud service providers offer a wide range of services, configurable policies, and security controls that help improve your overall cybersecurity posture and secure your digital assets.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Despite offering loads of benefits, cloud computing comes with a few pitfalls you should be aware of.
1. Vendor Lock-in
Whether you choose AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, you will receive all the tools and services needed to run any product and ensure scalability and security of operations. However, most of these features are platform-specific, so the more of them you sign up for, the harder it will be to move to another cloud service provider, should such a need arise in the future.
2. Misconfiguration
With dedicated servers, an error in configuration will exhaust the resources you have on-site. With cloud computing, a misconfiguration in scaling algorithms can lead to creating endless new instances and result in multi-million bills for resources you consumed while actually not needing them.
The solution is quite simple – entrusting your cloud computing management to people having relevant expertise, either by hiring them in-house or by partnering with third-party vendors. A skilled DevOps team from a reputed technology partner will advise on open-source components you can use instead of proprietary ones to avoid vendor lock-in, and configure vendor-specific tools correctly to ensure optimal cost-efficiency of your cloud operations.
Most such companies are listed on AWS Marketplace or similar boards of other cloud providers – or you can find such managed services cloud computing providers on Clutch, G2 crowd, Gartner, and other boards.
5. What is Cloud Computing for business?
Businesses. organizations and government agencies of all forms, sizes and in any industry can benefit from cloud computing in a wide range of scenarios, from data backup and recovery to email hosting, remote virtual desktops, content storage, Big Data analytics and Machine Learning, development and running various customer-facing apps.
For example, E-learning platforms of all sorts are best hosted in the cloud, due to it being a perfect medium for providing exactly the needed amount of resources to handle the workload of MOOCs and enabling the learners to safely and easily connect from any device, anywhere over the Internet.
Companies delivering data management and other Big Data services leverage the power of the cloud to help their customers with real-time decision-making and ongoing support of intense workloads.
Various enterprise Human Resource management tasks like application tracking, talent management, recruitment, payroll management, benefits administration, etc. Storing this data in the cloud ensures your HR department can securely work on it from anywhere.Let’s take a look at several use cases of cloud computing services for businesses.
- Cloud-native application development
Using cloud resources, services and platforms like Google App Engine developers can quickly build, release and run web, mobile and API applications. They also benefit from cloud-native DevOps tools and practices like Docker containers, Kubernetes clusters, Terraform or Pulumi manifests, Jenkins/Ansible CI/CD pipelines, microservices, API-driven communication, etc.
- Testing and building applications
Cloud resources are uniquely suited to quickly building test environments for your apps, greatly reducing overall time and costs spent on SDLC.
- Data storage, backup, and recovery
Your operational data is better handled at scale when it is automatically backed up, stored and recovered from several cloud locations over the internet.
- Data analytics
Use Artificial Intelligence algorithms and Machine Learning models to identify patterns within your historical data and detect any anomalies within your real-time data flows. This can help prevent a data breach or highlight a new revenue opportunity…
- Audio and video streaming
Stay in touch with your audience and scale up and down along with the numbers of your customers through multi-channel HD video and audio streaming services available on any device, globally.
- Embedded intelligence
Augment your customer journeys through smart assistants and gain actionable insights from behavioral data gathered
- Provide SaaS solutions
SaaS products benefit most from cloud computing due to the ability to run equally well for any customer and update to the latest versions seamlessly with the cloud high-availability features.
Questions to answer before moving your Data to the Cloud
Below is a list of questions every business should answer before making a decision to migrate their workloads and data to the cloud:
- How can I be sure my data is secure since it is not under my control?
- Is my data really accessible anytime?
- What is the failover mechanism?
- How can I ensure my provider delivers top-level cloud performance?
- Can I test their services to ensure I am getting the most out of my investments?
- Will I be able to shift my data and workloads between cloud regions effortlessly?
- How much would cloud transition lower my costs?
- Should I leave some software in-house or go full cloud to save on backup?
These decisions will help you select the most appropriate cloud vendor and deployment model for your case.
Summary
Transition to cloud computing and DevOps resulted in a real revolution in software delivery, IT, and business. It helped companies save on CAPEX and reduce OPEX, secure their critical data and forget about exceeding their capacities due to cloud scalability.
Cloud computing is here to stay, despite its pros and cons. It simply offers too many benefits to neglect it, to all types of users, from end customers of SaaS apps to developers, startups, or global corporations.
Academy Smart is among the leading software delivery and DevOps companies in Ukraine and it provides high-quality cloud-based services. With a focus on outstaffing and the ability to compose dedicated teams to meet the needs of particular projects, Academy Smart provides reliable cloud development expertise for various products:


If you need help defining the best cloud computing model to ensure your project’s success and continuous growth. Contact our cloud development experts who will be glad to clarify any nuance!
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!