Why Use Cloud Computing in Accounting
Contents
Cloud computing has revolutionized businesses’ operations, and the accounting industry is no exception. Cloud-based accounting software offers many benefits, including improved efficiency, scalability, and security. As a result, cloud computing is rapidly becoming the go-to solution for accounting firms of all sizes. This post demonstrates why your enterprise may also be interested in leveraging cloud accounting benefits.
What is Cloud Computing in Accounting
How do we define cloud computing in accounting? It is the use of internet-based technology to access and process financial data. Instead of relying on local servers or individual computer systems, third-party providers perform accounting functions on remote servers online. That enables real-time collaboration, accessibility from various locations, and the utilization of scalable resources based on business needs.
The adoption of cloud services in the accounting sector has evolved over the past decade. Initially, businesses hesitated due to concerns about data security and the unfamiliarity of entrusting financial information to external servers. However, as cloud service providers enhanced their security measures and demonstrated the operational advantages of their platforms, the accounting industry witnessed a gradual shift towards embracing cloud computing.
If we compare accounting in cloud computing with classic accounting software, we may find that:
- Traditional digital accounting often requires substantial initial investments in hardware and software licenses. In contrast, a cloud-based application typically operates on a subscription-based model, reducing upfront costs and providing scalability based on usage.
- Localized software usually limits access to a specific device or location. At the same time, cloud apps enable real-time access to financial data from any location with internet connectivity, fostering cooperation among geographically dispersed teams.
- Manual updates and maintenance are necessary for on-premise apps, leading to potential delays and disruptions. The cloud computing service provider manages automatic updates of cloud solutions, ensuring the latest features and security patches without user intervention.
- Traditional accounting apps usually provide narrow collaboration features, often requiring data consolidation and version control. Cloud-based software instead facilitates seamless collaboration among multiple users, reducing errors and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Scaling up an infrastructure of classic digital accounting can be complex and costly. Cloud accountant has on-demand scalability, allowing businesses to adjust resources based on evolving needs.
- Classic accounting software relies on the companies’ internal security measures, which may vary. Reputable cloud providers implement unified advanced security features, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits for their accounting or infrastructure services.
As cloud solutions continually evolve and are less susceptible to software obsolescence risks, more businesses are considering moving their accounting to the cloud as part of their digital transformation plan.
How cloud computing is used in accounting
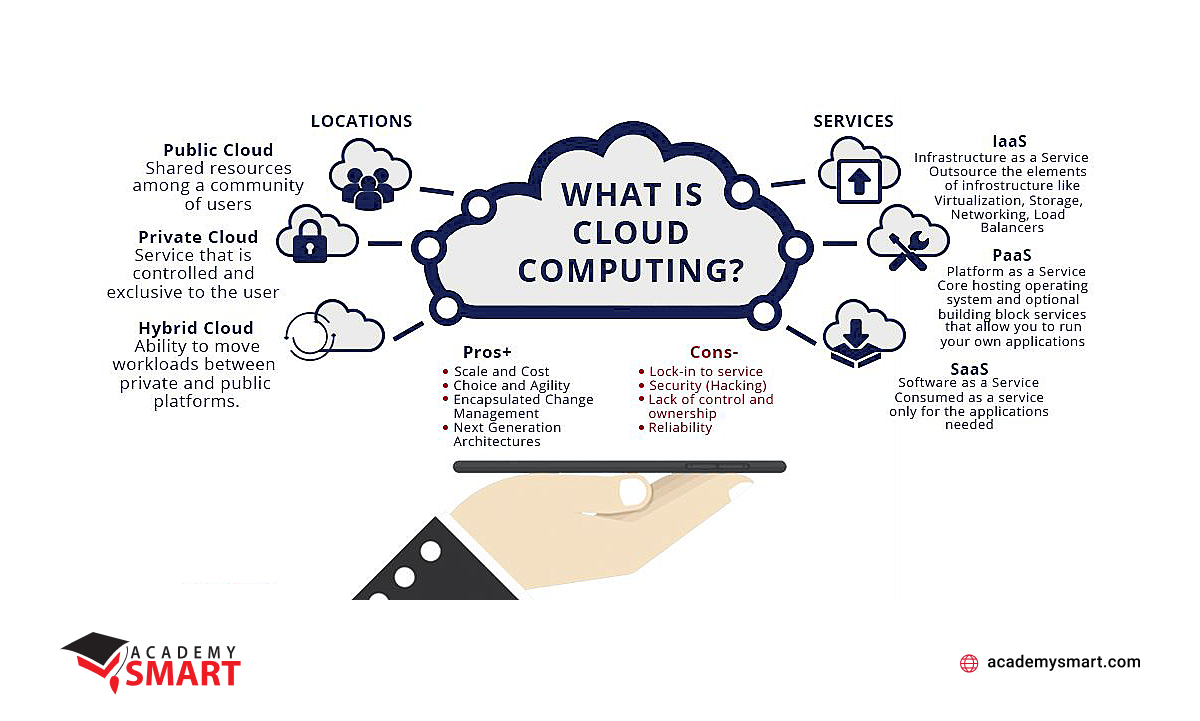
Each cloud service platform type – SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS – contributes specific features to enhance accounting processes.
Software-as-a-Service applications are most familiar to the average user. SaaS platforms offer cloud-based accounting software, providing comprehensive solutions for financial management. These tools, such as QuickBooks Online or Xero, facilitate tasks like invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting through a user-friendly interface. SaaS accounting solutions promote collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and work on financial data simultaneously. Real-time updates and access from various locations enhance teamwork and reduce the need for manual data consolidation.
With SaaS, businesses benefit from automatic updates delivered by the service provider. It ensures that accounting software runs the latest version, incorporating new features, security patches, and improvements without user intervention. Moreover, SaaS apps operate on a subscription-based pricing model, eliminating the need for upfront investments in software licenses. This cost-effective approach allows enterprises to pay for their actual services, encouraging financial efficiency.
Platform-as-a-Service provides a foundation for developing and customizing accounting applications. Businesses can tailor financial management tools to meet unique business requirements, creating a more personalized and efficient accounting IT system.
PaaS allows for scalable application development. As accounting needs evolve, organizations can scale their custom solutions without the complexity of managing the underlying infrastructure, ensuring that their IT platform grows alongside the business. In addition, PaaS solutions facilitate structured API integration with other business applications. Accounting platforms developed on PaaS can easily connect with Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), or other tools, streamlining data flow across the company.
At last, Infrastructure-as-a-Service supplies the fundamental computing infrastructure required for accounting processes. That includes virtual machines, storage, and networking resources, allowing organizations to scale computing power based on demand. IaaS operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing organizations to allocate computing resources based on actual usage. This cost-efficiency eliminates the need for extensive start-up expenses in hardware and fosters financial flexibility.
IaaS platforms enhance disaster recovery capabilities. By leveraging cloud-based backups and redundancy options, organizations can ensure the availability of financial data even in the face of unexpected events. Not less importantly, IaaS providers like AWS, GCP, or Azure offer robust security features, including encryption and compliance tools. That ensures the confidentiality and integrity of financial data, addressing regulatory requirements and industry standards.
What is cloud computing, and how does it work
Cloud Computing in Accounting: Pros and Cons
Usually, the CFO and CEO are responsible for financial actions regarding cloud computing implementation into accounting, so they must consider the advantages and disadvantages of such a decision.
Benefits of cloud accounting
Cloud accounting allows users to access financial data and software applications online from anywhere. Cloud accounting solutions are often accessible through web browsers or dedicated applications, making it convenient for users to manage financial tasks on various devices, including smartphones and tablets. This accessibility is especially beneficial for remote work and collaboration among team members in different locations.
The cloud service provider regularly updates cloud-based accounting software or its infrastructure. That ensures clients can access the latest features, improvements, and security patches without manual updates. Cloud services automatically back up financial data, reducing the risk of data loss in the event of hardware failures or other unforeseen circumstances. Cloud platforms also often provide robust disaster recovery capabilities.
Whether handling increased workloads during peak times or expanding business operations, enterprises can easily adjust their computing resources. The cost-efficient approach allows users to pay just for used computational services.
Cloud computing issues in accounting information systems
Companies relinquish some level of direct control over their infrastructure and data when moving to the cloud. Depending on the deployment model (public, private, or hybrid), organizations may need to trust their cloud service provider to manage and secure their accounting systems effectively. Moreover, cloud computing introduces challenges in ensuring that data stored and processed in the cloud complies with regional and industry-specific regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA. Implementing robust security measures and choosing reputed cloud service providers are crucial in mitigating unauthorized access, data breaches, or compromising sensitive financial information risks.
Some cloud accounting solutions may have limitations in terms of customization to meet specific organizational needs. This lack of flexibility can concern enterprises with unique accounting requirements that may not align with standardized cloud offerings. Transferring large volumes of financial data to the cloud and migrating from legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming. Integrating cloud accounting systems with existing on-premises applications or other cloud-based tools can pose challenges, too. Compatibility issues, data transfer complexities, and seamless system interoperability require careful planning and implementation.
Adopting a specific cloud service provider may lead to vendor lock-in, making it challenging to switch to a different provider or revert to an on-premises solution. Organizations need to assess the long-term implications and consider strategies to mitigate the risks associated with vendor lock-in. In addition, cloud service outages or downtime can disrupt accounting operations, potentially leading to delays in financial reporting and transactions. Companies must carefully consider the reliability and service level agreements (SLAs) offered by cloud providers to minimize the impact of potential disturbances.
While cloud computing can offer cost savings, organizations must manage their cloud expenses effectively. Uncontrolled usage or unexpected resource scaling can lead to higher-than-anticipated costs. Establishing transparent budgeting and monitoring practices is essential for financial control. Moreover, shifting to cloud-based accounting systems may require employees to adapt to new interfaces and workflows. Adequate training and change management strategies are crucial to maximize the benefits of cloud computing.
To make the path to cloud accounting as easy as possible, you may need a reliable and technically competent journey companion with expertise in cloud technologies. Our clients are confident that Academy Smart is such.

Portfolio of Academy Smart
How can Academy Smart Unlock the Benefits of Cloud Accounting
Smart Academy has aided enterprises with cloud adoption and migration for over 13 years. In our team, you will find IT specialists with vast practical experience in creating and deploying custom cloud applications of any level of complexity based on Amazon AWS and Microsoft Azure. With us, you can hire a dedicated team of developers to complete the entire project or specific IT experts to augment your internal staff. Do you need to move your accounting to the cloud? Contact us, and we will provide a solution to benefit your business.
Frequently Asked Questions: Accounting Services in Cloud Computing
How do I implement cloud accounting?
- select a respected cloud accounting software provider or develop your own,
- migrate financial data to the cloud,
- configure settings to meet enterprise needs,
- train staff to use a new app for daily accounting operations.
How much do cloud accounting services cost?
Cloud accounting software costs vary depending on the provider and the features included. However, most cloud computing services for accounting are available for a monthly fee of around $20 to $100.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!