What is Cloud Migration: benefits, types and strategies
Contents
The migration to the cloud is a responsible step for any business looking to stay competitive in today’s digitalized world. However, making the switch to cloud computing comes with its own set of challenges and common mistakes that can derail your efforts. If you’re considering turning to cloud services as a solution for your business, read on to learn more!
This article will discuss the importance of cloud migration for businesses, the potential obstacles you might encounter, and how to make sure your transition goes as smoothly as possible. By the end of the article, you’ll have a better understanding of the benefits of migrating to the cloud and the steps you can take to ensure a successful transition.
What is Cloud Migration
So, what is cloud migration? It is the process of moving data, applications and other business elements from an organization’s on-premise systems to a cloud-based environment. This process can be used to move software or data to a public, private or hybrid cloud structure, depending on the individual needs of the enterprise. Cloud migration can also be used to move from one cloud service to another.
The primary benefit of cloud migration is the ability to scale computing power, storage and other resources as required, allowing to quickly and efficiently accommodate changing needs or sudden increases in demand. It can help to reduce costs and enable businesses to operate more efficiently.
Migration to the cloud also allows businesses to access the latest technologies and services, as well as support from the cloud provider. It may reduce the need for in-house IT staff as the cloud provider takes on the responsibility for managing the infrastructure.
Why is Cloud Migration needed
Well, let’s check why migration in the cloud may be profitable for your business.
- Cost savings. Cloud services are typically priced on a pay-as-you-go model, which can help businesses save money as they scale and adjust to changing needs. Cloud migrations may significantly reduce the cost of maintaining and updating software, hardware, and other IT infrastructure.
- Increased productivity. By migrating to the cloud, a company can eliminate the need for manual tasks associated with on-premises systems, freeing up valuable time and resources. Cloud-based software and applications can also be accessed from anywhere, enabling employees to work remotely and collaborate more efficiently.
- Improved security. Cloud providers typically offer enterprise-grade security features, including encryption and identity management, which can help businesses protect their data from unauthorized access. In addition, cloud services are often more resilient to security threats than traditional on-premises systems.
- Greater flexibility. Cloud migration helps businesses rapidly respond to changing customer needs and market conditions. Cloud services can be quickly scaled up or down, enabling enterprises to deploy swiftly or decommission services as needed. It makes it easier for companies to quickly expand their operations without investing in more infrastructure.
What are the benefits of Cloud Migration
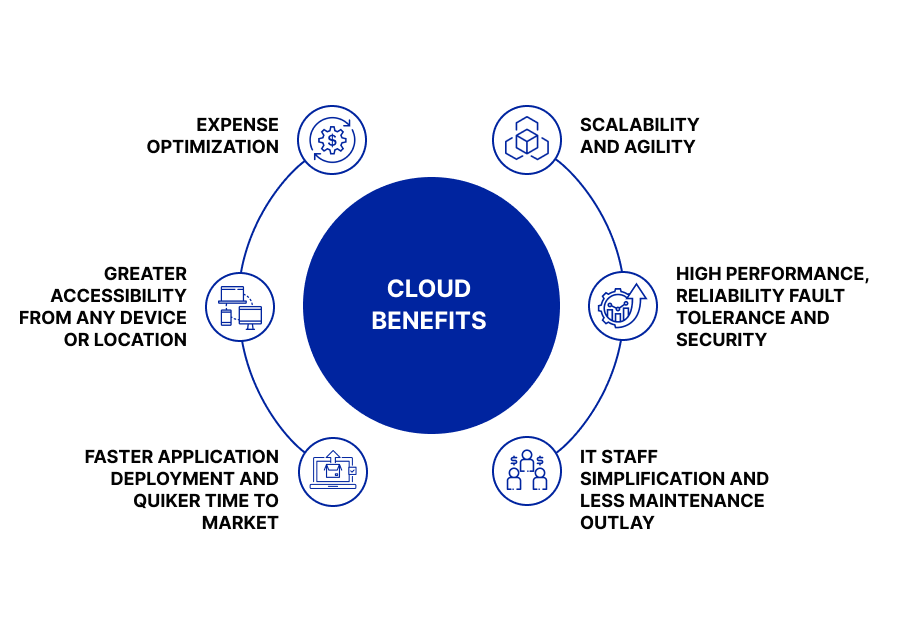
Migration in cloud is an excellent way to increase a business’s IT infrastructure’s scalability, reliability, and security. Let’s discuss the essential benefits of cloud migration in detail.
Expense optimization
The transition from CapEx to OpEx is a significant advantage of cloud migration. With CapEx, businesses must make upfront investments in local IT infrastructure and software, which can be costly. OpEx, on the other hand, allows companies to pay for IT services and resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. Migrating to the cloud, enterprises only pay for the resources they use, which enables them to save money and get more bang for their buck. It can be especially profitable for companies that experience seasonal spikes in usage and traffic.
Scalability and agility
The cloud provides the flexibility to deploy new services and applications quickly. Cloud migration allows organizations to scale their workloads up or down as needed easily. That means cloud resources can be added or removed as required, enabling enterprises to respond rapidly to shifting clients needs. This agility helps companies remain competitive and respond to changing market conditions.
High performance, reliability, fault tolerance and security
Cloud platforms use automated resources to manage workloads, making apps highly available and responsive. Cloud infrastructure enhances applications’ performance to scale rapidly to meet user demand. It is designed to be resilient and redundant to have self-healing capabilities, keeping apps available online despite hardware failure. It allows applications to continue running without interruption, ensuring users can access data and services with minimal disruption.
Cloud infrastructure provides robust security and compliance capabilities, allowing organizations to ensure that data remains secure and compliant with industry and regulatory requirements. In addition, cloud platforms use various security tools and technologies to protect data, including encryption, access control, and identity and access management. For more in-depth advantages, see Cloud computing in Data management: challenges, practices, cases, and benefits in our blog.
IT staff simplification and less maintenance outlay
Automating server setup and maintenance tasks with cloud-based solutions can result in significant expense savings for the enterprise. By moving to the cloud, an organization can decrease the amount of IT staff managing the business’s IT operations. Additionally, the cost of maintaining an on-premise infrastructure can be greatly reduced by pay-as-you-go pricing models offered by the cloud.
Faster application deployment and quicker time to market
By leveraging the scalability, elasticity, and agility of cloud computing, organizations can quickly deploy applications and services in a fraction of the time it would take using the traditional on-premises infrastructure. On the one hand, this is a faster way to return on investment in a software product. On the other hand, your customers can benefit from new features and products faster, enabling them to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Greater accessibility from any device or location
Cloud computing allows users to easily share and access data from any device or location, so long as they have an internet connection. It makes it possible for teams to work together more efficiently and effectively, even when they are geographically dispersed.
Pros of migrating to the cloud for business
What are the challenges of Cloud Migration
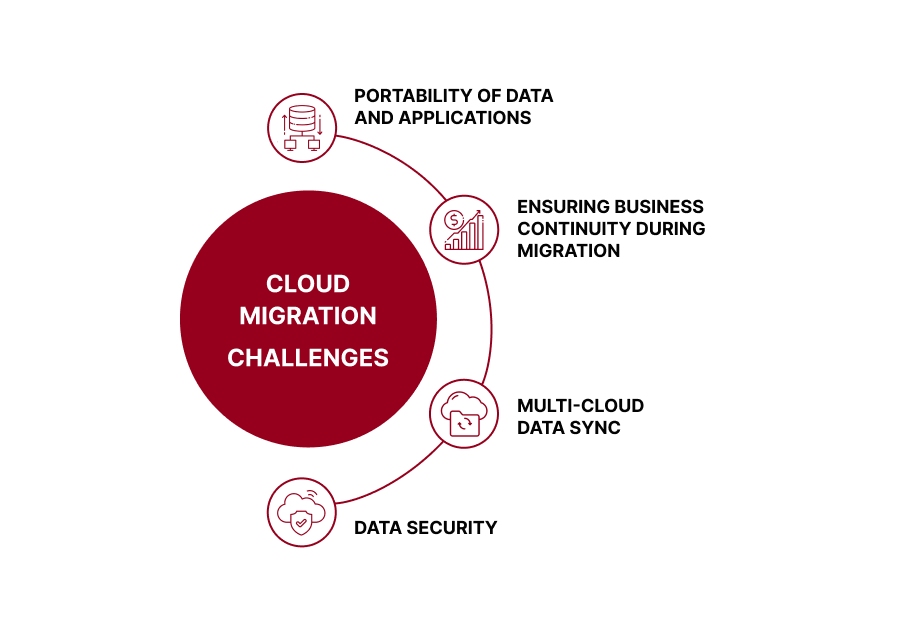
What challenges may you meet moving your business to the cloud? Migrating to the cloud can be complicated, especially for those with limited experience in cloud platforms. Proper planning is the key to a successful transition, and it is important to consider the scalability and availability of the cloud platform, as well as data security, cost, and performance. It is crucial to ensure that the migration process is well-documented and that all stakeholders are informed of the progress and changes throughout the process.
Portability of data and applications
It is not always possible to transfer the functionality of applications to the cloud without refining its code. Also, cloud infrastructures of providers (AWS Amazon, Google Cloud or Microsoft Azure, etc.) often have very different architectures, configurations, and security protocols and policies. That can complicate transferring data and applications from on-premises or one cloud provider to another. It requires specific modifications or re-architecting of software to work correctly in different cloud environments.
Data security
Since organizations relinquish their data to a third-party provider, they must trust the provider to secure their data from unauthorized access, malicious actors, and other cyber threats. Cloud computing environments can be too complex and difficult to secure, so the business may need additional efforts to configure and maintain safety measures for their data and applications. Finally, cloud migrations can introduce compliance issues, as enterprises must adhere to changing regulations and industry standards to protect their data.
Multi-cloud data sync
Your business goals may need migration in several clouds at once. But it’s not easy to ensure that data is synchronized across multiple cloud environments, as each cloud provider may have different data storage and transfer protocols. Furthermore, cloud providers may charge different service prices, making finding a cost-effective multi-cloud data sync solution challenging. Additionally, due to the complexity of the cloud environments, it may be hard to maintain a consistent security strategy and industry regulations compliant.
Ensuring business continuity during migration
The cloud environment is constantly changing and evolving, so enterprises must adapt, update and change their strategies quickly to keep up with the latest developments. Finally, a business must consider the price of cloud tech implementation and its potential impact on the bottom line. The cloud is often cheaper than on-premise solutions, but the cost of migration, storage, and other services can add up quickly.
Main business challenges of migration in the cloud
What are the types of cloud migration
When you plan to move data, applications, and other computing resources from a traditional on-premises environment to a cloud-based one, you must choose the way that suits your business goals.
There are several types of cloud migration targets, including public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Public cloud solutions allow businesses to quickly access and use various cloud services, while private cloud solutions provide enterprises with greater control and security over their data. Hybrid cloud solutions combine the flexibility of public cloud solutions with the security of private cloud solutions.
Additionally, you can also choose from different models of cloud services such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). With all these options, businesses may select the cloud that best meets their needs.
Migration to the IaaS cloud
IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service) is a cloud computing service that provides users with access to virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking. With IaaS, users can quickly deploy and scale their applications without purchasing and managing physical hardware. IaaS is typically billed on a pay-as-you-go basis and offers users the flexibility to scale up or down as needed quickly. The cloud environment also improves security, availability, and disaster recovery.
Migration to the PaaS cloud
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides users with a platform for developing and deploying applications. With PaaS, users no longer need to worry about managing hardware or software infrastructure, as this is done by the cloud provider. PaaS offers users the ability to quickly build, deploy, and scale applications, as well as access to a wide range of development tools and services. PaaS also allows for rapid deployment of apps across multiple cloud environments, enabling users to quickly take advantage of new technologies and services.
Migration to the SaaS cloud
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is a type of cloud computing service that provides users with access to applications and software over the internet. SaaS offers users the ability to quickly access and use the latest software and the flexibility to scale up or down as needed. With SaaS, users no longer need to install and manage software on their computers. Instead, applications are delivered and managed through the cloud, allowing users to access them from any device with an internet connection.
Main types of Cloud services for migration
Cloud Migration strategies
We can use several strategies to migrate our applications and data to the cloud. Different approaches may be more suitable depending on the type of software and the needs of the business. For example, an enterprise may choose to lift-and-shift its existing applications to the cloud, or it may opt to re-architect its applications to take advantage of the cloud’s capabilities. Each approach has its benefits and challenges, so businesses should carefully consider their options before deciding.
Rehosting
The Lift-and-Shift or Rehosting strategy is the simplest way of cloud migration when existing applications and data are moved from an on-premises environment to the cloud without making any changes to the underlying architecture.
This strategy is often used when a business needs to quickly move its applications and data to the cloud with no wasting time or resources to make significant modifications. It is also helpful for companies that want to test the cloud services possibilities and start the migration process without making any big changes.
Rearchitecting
Re-architecting is the process of modifying existing software to take full advantage of the features and capabilities of the cloud. That typically involves making changes to the underlying architecture of the application to improve scalability and performance. Re-architecting may involve rethinking the app design, such as using containers or microservices instead of traditional monolithic applications or using serverless computing instead of virtualized servers.
Replatforming
The replatforming strategy is a type of cloud migration in which an existing application is moved to a different platform or technology stack. Replacing involves moving an application to another cloud provider or taking advantage of new features offered by the cloud. This article discusses how the software platform and technology stack are interconnected – How To Choose Technology Stack: Clients Guide.
Rebuilding
Rebuilding involves completely rewriting an application to take full advantage of the features and capabilities of cloud calculations. It typically involves the most radical changes in the app’s design, code, and architecture. Rebuilding can be beneficial if the new cloud platform offers better performance, security, or costs. Rebuilding can be a complex and long-time process, but it can yield the greatest benefits for a business’s cloud migration.
Repurchasing
Repurchasing is the process of buying some cloud services to use instead of existing on-premises services. Usually, no changes to local applications are needed. By purchasing new cloud services, a company can quickly access popular technologies and services that have features analog to the on-premises apps they own. Repurchasing can be cost-effective, but it may be rushed and not consider the latest technological capabilities available from the cloud providers.
Retiring
Retire is a strategy of canceling the migration in the cloud for some parts of your application and transferring only ones that are still used or needed. It can help reduce costs and free up resources for other projects. It’s helpful to reduce software complexity and improve the security of your services.
Retaining
Retaining can be a good decision if the migration is not proceeding as expected or if its cost is higher than expected. It may include keeping existing users, usage patterns, and cost measures in place, or it may mean reverting to an older version of the cloud software with better features and cost-efficiency.
At the same time, experts usually re-evaluate the effectiveness of each component to find weaknesses and unreasonably expensive software parts or features. This process helps ensure that the app will be optimized for the cloud and running as efficiently as possible.
In our presentation below, you can see what the cloud applications developed by Academy Smart look like.
Cloud Migration Process: 7 step
The number of steps a company needs to take to migrate to the cloud can vary depending on various factors, such as the size of the company, the complexity of its infrastructure, the type of workloads to be migrated, and the cloud service provider’s choices. However, a general outline of the steps involved in a cloud migration process could include the following:
- Assessment of current infrastructure and workloads;
- Selection of a cloud service provider;
- Design of a cloud migration plan and strategy;
- Preparation of the environment and data for migration;
- Implementation of the migration plan;
- Testing and validation of the migration;
- Ongoing monitoring and management of the cloud environment.
It’s important to note that this is a high-level overview, and the specifics of the migration process can vary greatly depending on the company’s specific needs and requirements. Working with experienced cloud migration professionals is also recommended to ensure a successful and efficient moving process.
Step 1. Assessment of current infrastructure and workloads
This step involves thoroughly evaluating the company’s existing IT infrastructure and workloads to determine what needs to be migrated to the cloud and the potential impact on the business. It includes assessing the current hardware and software setup, data and storage requirements, and application dependencies.
Step 2. Selection of a cloud service provider
In this step, the company chooses a cloud service provider that aligns with its business needs, goals, and budget. Factors to consider include security, data privacy, reliability, scalability, and support.
Step 3. Design of a cloud migration plan and strategy
This step includes creating a detailed plan and strategy for the migration in the cloud, including identifying and mitigating potential risks, outlining the timeline and milestones, and determining the resources needed.
Step 4. Preparation of the environment and data for migration
At that stage, preparing the company’s existing environment and data for migration to the cloud is going. It may include cleaning up and optimizing data, updating or re-architecting applications, and establishing connectivity between the current infrastructure and the cloud.
Step 5. Implementation of the migration plan
The company executes the migration plan and moves the workloads and data to the cloud. At this step, configuring the cloud environment, migrating the data, and deploying the applications are provided.
Step 6. Testing and validation of the migration
This step thoroughly tests the migrated workloads and data to ensure they function as expected in the cloud environment. It includes performing functional and non-functional testing, verifying that data has been migrated accurately, and ensuring that all application dependencies are working as intended.
Step 7. Ongoing monitoring and management of the cloud environment
Effective ongoing management is essential to ensure the success of the cloud migration and realize the benefits of that move. Once the migration is complete, the company must continuously monitor and manage the cloud environment to ensure it remains secure, reliable, and efficient. It includes performing regular security audits, monitoring resource usage and performance, and making updates and upgrades to ensure the cloud environment meets the company’s needs.
The migration in the cloud is a complex and technically demanding task requiring specialized expertise and significant resources. To ensure the successful implementation of business plans, the assistance of cloud technology experts is often necessary. Academy Smart has a proven track record of delivering high-quality results, as demonstrated by this example of a cloud services management platform.

Cloud services management platform we have developed
How Academy SMART can help you in Cloud Migration
Academy Smart has extensive expertise in developing cloud applications on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud and supporting cloud migrations for our clients. Our range of services includes:
- DevOps outstaffing;
- CI/CD services;
- Secure serverless application development;
- In-depth cloud business intelligence.
If you’re looking to maximize the value of your cloud application, let’s discuss your business goals and determine the ideal solution for your needs.
Cloud migrations: Frequently Asked Questions
What are Common Cloud Migration Challenges?
Migrating to the cloud can be challenging due to the complexity of transitioning existing applications, data, and infrastructure and ensuring compliance with security policies.
What are the key benefits for cloud transformation?
The main benefits of cloud migration you may get with our assistance are the following:
- increased flexibility;
- cost savings;
- enhanced reliability;
- increased efficiency;
- improved collaboration and data sharing.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!